Earthquakes May Endanger New York More Than Thought, Says Study
A study by a group of prominent seismologists suggests that a pattern of subtle but active faults makes the risk of earthquakes to the New York City area substantially greater than formerly believed. Among other things, they say that the controversial Indian Point nuclear power plants, 24 miles north of the city, sit astride the previously unidentified intersection of two active seismic zones. The paper appears in the current issue of the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America.
Many faults and a few mostly modest quakes have long been known around New York City, but the research casts them in a new light. The scientists say the insight comes from sophisticated analysis of past quakes, plus 34 years of new data on tremors, most of them perceptible only by modern seismic instruments. The evidence charts unseen but potentially powerful structures whose layout and dynamics are only now coming clearer, say the scientists. All are based at Columbia University’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, which runs the network of seismometers that monitors most of the northeastern United States.
Lead author Lynn R. Sykes said the data show that large quakes are infrequent around New Yorkcompared to more active areas like California and Japan, but that the risk is high, because of the overwhelming concentration of people and infrastructure. “The research raises the perception both of how common these events are, and, specifically, where they may occur,” he said. “It’s an extremely populated area with very large assets.” Sykes, who has studied the region for four decades, is known for his early role in establishing the global theory of plate tectonics.
The authors compiled a catalog of all 383 known earthquakes from 1677 to 2007 in a 15,000-square-mile area around New York City. Coauthor John Armbruster estimated sizes and locations of dozens of events before 1930 by combing newspaper accounts and other records. The researchers say magnitude 5 quakes—strong enough to cause damage–occurred in 1737, 1783 and 1884. There was little settlement around to be hurt by the first two quakes, whose locations are vague due to a lack of good accounts; but the last, thought to be centered under the seabed somewhere between Brooklyn and Sandy Hook, toppled chimneys across the city and New Jersey, and panicked bathers at Coney Island. Based on this, the researchers say such quakes should be routinely expected, on average, about every 100 years. “Today, with so many more buildings and people, a magnitude 5 centered below the city would be extremely attention-getting,” said Armbruster. “We’d see billions in damage, with some brick buildings falling. People would probably be killed.”
Starting in the early 1970s Lamont began collecting data on quakes from dozens of newly deployed seismometers; these have revealed further potential, including distinct zones where earthquakes concentrate, and where larger ones could come. The Lamont network, now led by coauthor Won-Young Kim, has located hundreds of small events, including a magnitude 3 every few years, which can be felt by people at the surface, but is unlikely to cause damage. These small quakes tend to cluster along a series of small, old faults in harder rocks across the region. Many of the faults were discovered decades ago when subways, water tunnels and other excavations intersected them, but conventional wisdom said they were inactive remnants of continental collisions and rifting hundreds of millions of years ago. The results clearly show that they are active, and quite capable of generating damaging quakes, said Sykes.
One major previously known feature, the Ramapo Seismic Zone, runs from eastern Pennsylvania to the mid-Hudson Valley, passing within a mile or two northwest of Indian Point. The researchers found that this system is not so much a single fracture as a braid of smaller ones, where quakes emanate from a set of still ill-defined faults. East and south of the Ramapo zone—and possibly more significant in terms of hazard–is a set of nearly parallel northwest-southeast faults. These include Manhattan’s 125th Street fault, which seems to have generated two small 1981 quakes, and could have been the source of the big 1737 quake; the Dyckman Street fault, which carried a magnitude 2 in 1989; the Mosholu Parkway fault; and the Dobbs Ferry fault in suburban Westchester, which generated the largest recent shock, a surprising magnitude 4.1, in 1985. Fortunately, it did no damage. Given the pattern, Sykes says the big 1884 quake may have hit on a yet-undetected member of this parallel family further south.
The researchers say that frequent small quakes occur in predictable ratios to larger ones, and so can be used to project a rough time scale for damaging events. Based on the lengths of the faults, the detected tremors, and calculations of how stresses build in the crust, the researchers say that magnitude 6 quakes, or even 7—respectively 10 and 100 times bigger than magnitude 5–are quite possible on the active faults they describe. They calculate that magnitude 6 quakes take place in the area about every 670 years, and sevens, every 3,400 years. The corresponding probabilities of occurrence in any 50-year period would be 7% and 1.5%. After less specific hints of these possibilities appeared in previous research, a 2003 analysis by The New York City Area Consortium for Earthquake Loss Mitigation put the cost of quakes this size in the metro New York area at $39 billion to $197 billion. A separate 2001 analysis for northern New Jersey’s Bergen County estimates that a magnitude 7 would destroy 14,000 buildings and damage 180,000 in that area alone. The researchers point out that no one knows when the last such events occurred, and say no one can predict when they next might come.
“We need to step backward from the simple old model, where you worry about one large, obvious fault, like they do in California,” said coauthor Leonardo Seeber. “The problem here comes from many subtle faults. We now see there is earthquake activity on them. Each one is small, but when you add them up, they are probably more dangerous than we thought. We need to take a very close look.” Seeber says that because the faults are mostly invisible at the surface and move infrequently, a big quake could easily hit one not yet identified. “The probability is not zero, and the damage could be great,” he said. “It could be like something out of a Greek myth.”
The researchers found concrete evidence for one significant previously unknown structure: an active seismic zone running at least 25 miles from Stamford, Conn., to the Hudson Valley town of Peekskill, N.Y., where it passes less than a mile north of the Indian Point nuclear power plant. The Stamford-Peekskill line stands out sharply on the researchers’ earthquake map, with small events clustered along its length, and to its immediate southwest. Just to the north, there are no quakes, indicating that it represents some kind of underground boundary. It is parallel to the other faults beginning at 125th Street, so the researchers believe it is a fault in the same family. Like the others, they say it is probably capable of producing at least a magnitude 6 quake. Furthermore, a mile or so on, it intersects the Ramapo seismic zone.
Sykes said the existence of the Stamford-Peekskill line had been suggested before, because the Hudson takes a sudden unexplained bend just ot the north of Indian Point, and definite traces of an old fault can be along the north side of the bend. The seismic evidence confirms it, he said. “Indian Point is situated at the intersection of the two most striking linear features marking the seismicity and also in the midst of a large population that is at risk in case of an accident,” says the paper. “This is clearly one of the least favorable sites in our study area from an earthquake hazard and risk perspective.”
The findings comes at a time when Entergy, the owner of Indian Point, is trying to relicense the two operating plants for an additional 20 years—a move being fought by surrounding communities and the New York State Attorney General. Last fall the attorney general, alerted to the then-unpublished Lamont data, told a Nuclear Regulatory Commission panel in a filing: “New data developed in the last 20 years disclose a substantially higher likelihood of significant earthquake activity in the vicinity of [Indian Point] that could exceed the earthquake design for the facility.” The state alleges that Entergy has not presented new data on earthquakes past 1979. However, in a little-noticed decision this July 31, the panel rejected the argument on procedural grounds. A source at the attorney general’s office said the state is considering its options.
The characteristics of New York’s geology and human footprint may increase the problem. Unlike in California, many New York quakes occur near the surface—in the upper mile or so—and they occur not in the broken-up, more malleable formations common where quakes are frequent, but rather in the extremely hard, rigid rocks underlying Manhattan and much of the lower Hudson Valley. Such rocks can build large stresses, then suddenly and efficiently transmit energy over long distances. “It’s like putting a hard rock in a vise,” said Seeber. “Nothing happens for a while. Then it goes with a bang.” Earthquake-resistant building codes were not introduced to New York City until 1995, and are not in effect at all in many other communities. Sinuous skyscrapers and bridges might get by with minimal damage, said Sykes, but many older, unreinforced three- to six-story brick buildings could crumble.
Art Lerner-Lam, associate director of Lamont for seismology, geology and tectonophysics, pointed out that the region’s major highways including the New York State Thruway, commuter and long-distance rail lines, and the main gas, oil and power transmission lines all cross the parallel active faults, making them particularly vulnerable to being cut. Lerner-Lam, who was not involved in the research, said that the identification of the seismic line near Indian Point “is a major substantiation of a feature that bears on the long-term earthquake risk of the northeastern United States.” He called for policymakers to develop more information on the region’s vulnerability, to take a closer look at land use and development, and to make investments to strengthen critical infrastructure.
“This is a landmark study in many ways,” said Lerner-Lam. “It gives us the best possible evidence that we have an earthquake hazard here that should be a factor in any planning decision. It crystallizes the argument that this hazard is not random. There is a structure to the location and timing of the earthquakes. This enables us to contemplate risk in an entirely different way. And since we are able to do that, we should be required to do that.”
New York Earthquake Briefs and Quotes:
Existing U.S. Geological Survey seismic hazard maps show New York City as facing more hazard than many other eastern U.S. areas. Three areas are somewhat more active—northernmost New York State, New Hampshire and South Carolina—but they have much lower populations and fewer structures. The wider forces at work include pressure exerted from continuing expansion of the mid-Atlantic Ridge thousands of miles to the east; slow westward migration of the North American continent; and the area’s intricate labyrinth of old faults, sutures and zones of weakness caused by past collisions and rifting.
Due to New York’s past history, population density and fragile, interdependent infrastructure, a 2001 analysis by the Federal Emergency Management Agency ranks it the 11th most at-risk U.S. city for earthquake damage. Among those ahead: Los Angeles, San Francisco, Seattle and Portland. Behind: Salt Lake City, Sacramento, Anchorage.
New York’s first seismic station was set up at Fordham University in the 1920s. Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, in Palisades, N.Y., has operated stations since 1949, and now coordinates a network of about 40.
Dozens of small quakes have been felt in the New York area. A Jan. 17, 2001 magnitude 2.4, centered in the Upper East Side—the first ever detected in Manhattan itself–may have originated on the 125th Street fault. Some people thought it was an explosion, but no one was harmed.
The most recent felt quake, a magnitude 2.1 on July 28, 2008, was centered near Milford, N.J. Houses shook and a woman at St. Edward’s Church said she felt the building rise up under her feet—but no damage was done.
Questions about the seismic safety of the Indian Point nuclear power plant, which lies amid a metropolitan area of more than 20 million people, were raised in previous scientific papers in 1978 and 1985.
Because the hard rocks under much of New York can build up a lot strain before breaking, researchers believe that modest faults as short as 1 to 10 kilometers can cause magnitude 5 or 6 quakes.
In general, magnitude 3 quakes occur about 10 times more often than magnitude fours; 100 times more than magnitude fives; and so on. This principle is called the Gutenberg-Richter relationship.
The prophecy is more than seeing into the future. For the prophecy sees without the element of time. For the prophecy sees things as they were, as they are, and as they always shall be.
Tuesday, October 31, 2023
Columbia University Warns Of Sixth Seal (Revelation 6:12)
Monday, October 30, 2023
The Sixth Seal Long Overdue (Revelation 6)
The Big One Awaits
By MARGO NASH
Published: March 25, 2001
Alexander Gates, a geology professor at Rutgers-Newark, is co-author of “The Encyclopedia of Earthquakes and Volcanoes,“ which will be published by Facts on File in July. He has been leading a four-year effort to remap an area known as the Sloatsburg Quadrangle, a 5-by-7-mile tract near Mahwah that crosses into New York State. The Ramapo Fault, which runs through it, was responsible for a big earthquake in 1884, and Dr. Gates warns that a recurrence is overdue. He recently talked about his findings.
Q. What have you found?
A. We’re basically looking at a lot more rock, and we’re looking at the fracturing and jointing in the bedrock and putting it on the maps. Any break in the rock is a fracture. If it has movement, then it’s a fault. There are a lot of faults that are offshoots of the Ramapo. Basically when there are faults, it means you had an earthquake that made it. So there was a lot of earthquake activity to produce these features. We are basically not in a period of earthquake activity along the Ramapo Fault now, but we can see that about six or seven times in history, about 250 million years ago, it had major earthquake activity. And because it’s such a fundamental zone of weakness, anytime anything happens, the Ramapo Fault goes.
Q. Where is the Ramapo Fault?
A. The fault line is in western New Jersey and goes through a good chunk of the state, all the way down to Flemington. It goes right along where they put in the new 287. It continues northeast across the Hudson River right under the Indian Point power plant up into Westchester County. There are a lot of earthquakes rumbling around it every year, but not a big one for a while.
Q. Did you find anything that surprised you?
A. I found a lot of faults, splays that offshoot from the Ramapo that go 5 to 10 miles away from the fault. I have looked at the Ramapo Fault in other places too. I have seen splays 5 to 10 miles up into the Hudson Highlands. And you can see them right along the roadsides on 287. There’s been a lot of damage to those rocks, and obviously it was produced by fault activities. All of these faults have earthquake potential.
Q. Describe the 1884 earthquake.
A. It was in the northern part of the state near the Sloatsburg area. They didn’t have precise ways of describing the location then. There was lots of damage. Chimneys toppled over. But in 1884, it was a farming community, and there were not many people to be injured. Nobody appears to have written an account of the numbers who were injured.
Q. What lessons we can learn from previous earthquakes?
A. In 1960, the city of Agadir in Morocco had a 6.2 earthquake that killed 12,000 people, a third of the population, and injured a third more. I think it was because the city was unprepared.There had been an earthquake in the area 200 years before. But people discounted the possibility of a recurrence. Here in New Jersey, we should not make the same mistake. We should not forget that we had a 5.4 earthquake 117 years ago. The recurrence interval for an earthquake of that magnitude is every 50 years, and we are overdue. The Agadir was a 6.2, and a 5.4 to a 6.2 isn’t that big a jump.
Q. What are the dangers of a quake that size?
A. When you’re in a flat area in a wooden house it’s obviously not as dangerous, although it could cut off a gas line that could explode. There’s a real problem with infrastructure that is crumbling, like the bridges with crumbling cement. There’s a real danger we could wind up with our water supplies and electricity cut off if a sizable earthquake goes off. The best thing is to have regular upkeep and keep up new building codes. The new buildings will be O.K. But there is a sense of complacency.
MARGO NASH
Here is the Sixth Seal Zone (Revelation 6:12)
April 13, 20204 Min Read
Let’s get able to (probably) rumble.
A report this week from the Los Angeles Instances took a have a look at what a devastating earthquake may do to Los Angeles — and the classes to be discovered from the calamitous 6.three magnitude quake in 2011 that every one however flattened Christchurch, New Zealand.
However whereas People are conscious of the San Andreas fault and the seismic exercise in California, which has wreaked havoc in San Francisco and Los Angeles, there are different, lesser-known fault traces in the United States that fly dangerously underneath the radar. These cracks in the crust have prompted appreciable harm in the previous — and scientists say will achieve this once more.
Virginia Seismic Zone
Richmond, VirginiaShutterstock
In 2011, New Yorkers had been jolted by a 5.eight magnitude earthquake that shook the East Coast from New Hampshire all the approach down by means of Chapel Hill, North Carolina. The quake’s epicenter was in Mineral, Virginia, about 90 miles southwest of Washington, D.C., and was so highly effective that Union Station, the Pentagon and the Capitol Constructing had been all evacuated.
The quake woke lots of people in the northeast as much as the Virginia Seismic Zone (VSZ) under the Mason Dixon — and the consequential results it may have on main cities alongside the East Coast. The final time the VSZ prompted a lot chaos was in 1867 when it launched an earthquake of 5.6-magnitude — the strongest in Virginia’s historical past.
Ramapo Fault Zone
Shutterstock
It’s not simply the Virginia Seismic Zone New Yorkers have to fret about. Nearer to house is the Ramapo Fault Zone, which stretches from New York by means of New Jersey to Pennsylvania and was most energetic tens of millions of years in the past throughout the formation of the Appalachian Mountains. It’s answerable for a number of of the fault traces that run by means of New York Metropolis, together with one underneath 125th Avenue. In line with a New York Publish report in 2017, “On common, the area has witnessed a reasonable quake (about a 5.zero on the Richter scale) each hundred years. The final one was in 1884. Seismologists say we will anticipate the subsequent one any day now.” Enjoyable occasions!
The New Madrid Seismic Zone
This 150 mile-long sequence of faults stretches underneath 5 states: Illinois, Missouri, Arkansas, Tennessee and Kentucky, and is answerable for 4 of the largest earthquakes in the historical past of the United States, which befell over three months from December 1811 and February 1812. The quakes had been so robust the mighty Mississippi River flowed backward for 3 days. Fortunately, the space was not as populated as it’s now, so the harm was restricted. Nonetheless, a FEMA report launched in 2008 warned {that a} quake now could be catastrophic and end in “the highest financial losses as a consequence of a pure catastrophe in the United States.”
The Northern Sangre de Cristo Fault
Downtown Trinidad, Colorado Shutterstock
In 2011, a magnitude 5.three quake hit Trinidad, Colorado, one other space that has seen little seismic exercise on such a big scale. In line with the Colorado Division of Homeland Safety and Emergency Administration, The Sangre de Cristo Fault, which lies at the base of the Sangre de Cristo Mountains alongside the japanese fringe of the San Luis Valley, and the Sawatch Fault, which runs alongside the japanese fringe of the Sawatch Vary, are “two of the most distinguished probably energetic faults in Colorado” and that “Seismologists predict that Colorado will once more expertise a magnitude 6.5 earthquake at some unknown level in the future.”
The Cascadia Subduction Zone
One in every of the most probably harmful fault traces lies north of California, stretching between Oregon and Washington. Main cities like Portland, Seattle and Vancouver lie alongside the Cascadia Subduction Zone, which scientists say has the functionality of a 9.zero or 10 magnitude earthquake — 16 occasions extra highly effective than the 1906 quake which ravaged San Francisco. A quake of this magnitude would have devastating penalties on infrastructure and will probably set off large tsunamis. The risk is so nice, the BBC even did a nifty video on the potential MegaQuake risk.Sunday, October 29, 2023
The History of Earthquakes In New York Before the Sixth Seal (Revelation 6:12)
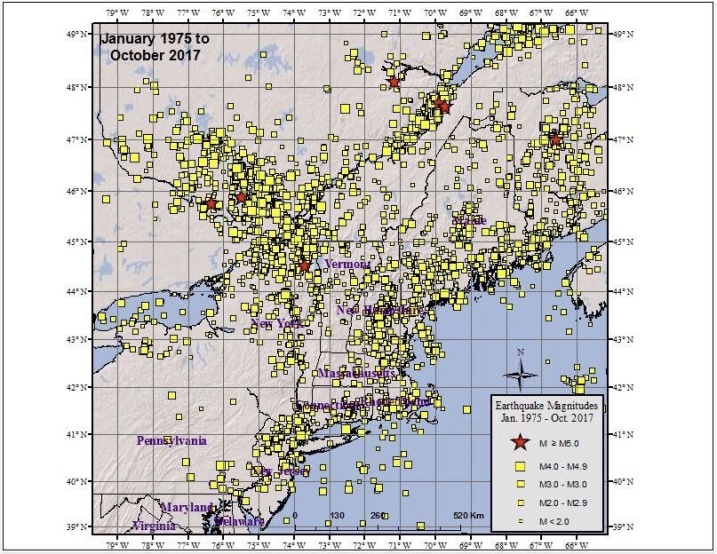 The History of Earthquakes In New York
The History of Earthquakes In New York
By Meteorologist Michael Gouldrick New York State PUBLISHED 6:30 AM ET Sep. 09, 2020 PUBLISHED 6:30 AM EDT Sep. 09, 2020
New York State has a long history of earthquakes. Since the early to mid 1700s there have been over 550 recorded earthquakes that have been centered within the state’s boundary. New York has also been shaken by strong earthquakes that occurred in southeast CaThe History of Earthquakes In New York Before the Sixth Seal (Revelation 6:12) nada and the Mid-Atlantic states.
Courtesy of Northeast States Emergency Consortium
A school gymnasium suffered major damage, some 90% of chimneys toppled over and house foundations were cracked. Windows broke and plumbing was damaged. This earthquake was felt from Maine to Michigan to Maryland.
Another strong quake occurred near Attica on August 12th, 1929. Chimneys took the biggest hit, foundations were also cracked and store shelves toppled their goods.
In more recent memory some of the strongest quakes occurred On April 20th, 2002 when a 5.0 rattled the state and was centered on Au Sable Forks area near Plattsburg, NY.
Strong earthquakes outside of New York’s boundary have also shaken the state. On February 5th, 1663 near Charlevoix, Quebec, an estimated magnitude of 7.5 occurred. A 6.2 tremor was reported in Western Quebec on November 1st in 1935. A 6.2 earthquake occurred in the same area on March 1st 1925. Many in the state also reported shaking on August 23rd, 2011 from a 5.9 earthquake near Mineral, Virginia.
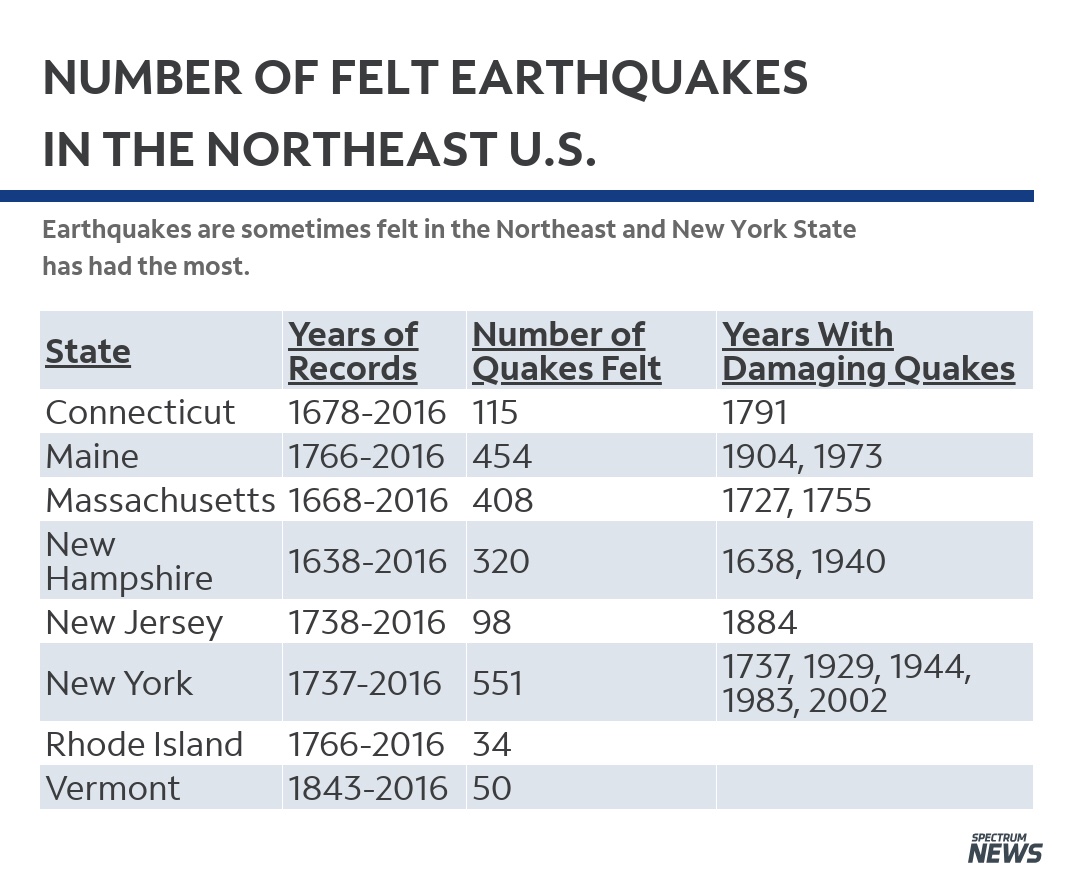
Earthquakes in the northeast U.S. and southeast Canada are not as intense as those found in other parts of the world but can be felt over a much larger area. The reason for this is the makeup of the ground. In our part of the world, the ground is like a jigsaw puzzle that has been put together. If one piece shakes, the whole puzzle shakes.
In the Western U.S., the ground is more like a puzzle that hasn’t been fully put together yet. One piece can shake violently, but only the the pieces next to it are affected while the rest of the puzzle doesn’t move.
In Rochester, New York, the most recent earthquake was reported on March 29th, 2020. It was a 2.6 magnitude shake centered under Lake Ontario. While most did not feel it, there were 54 reports of the ground shaking.
So next time you are wondering why the dishes rattled, or you thought you felt the ground move, it certainly could have been an earthquake in New York.
Here is a website from the USGS (United Sates Geologic Society) of current earthquakes greater than 2.5 during the past day around the world. As you can see, the Earth is a geologically active planet!
Another great website of earthquakes that have occurred locally can be found here.
To learn more about the science behind earthquakes, check out this website from the USGS.
Thursday, October 26, 2023
Economic Consequences of the Sixth Seal (Revelation 6:12)
Scenario Earthquakes for Urban Areas Along the Atlantic Seaboard of the United States
NYCEM.org
If today a magnitude 6 earthquake were to occur centered on New York City, what would its effects be? Will the loss be 10 or 100 billion dollars? Will there be 10 or 10,000 fatalities? Will there be 1,000 or 100,000 homeless needing shelter? Can government function, provide assistance, and maintain order?
At this time, no satisfactory answers to these questions are available. A few years ago, rudimentary scenario studies were made for Boston and New York with limited scope and uncertain results. For most eastern cities, including Washington D.C., we know even less about the economic, societal and political impacts from significant earthquakes, whatever their rate of occurrence.
Why do we know so little about such vital public issues? Because the public has been lulled into believing that seriously damaging quakes are so unlikely in the east that in essence we do not need to consider them. We shall examine the validity of this widely held opinion.
Is the public’s earthquake awareness (or lack thereof) controlled by perceived low Seismicity, Seismic Hazard, or Seismic Risk? How do these three seismic features differ from, and relate to each other? In many portions of California, earthquake awareness is refreshed in a major way about once every decade (and in some places even more often) by virtually every person experiencing a damaging event. The occurrence of earthquakes of given magnitudes in time and space, not withstanding their effects, are the manifestations of seismicity. Ground shaking, faulting, landslides or soil liquefaction are the manifestations of seismic hazard. Damage to structures, and loss of life, limb, material assets, business and services are the manifestations of seismic risk. By sheer experience, California’s public understands fairly well these three interconnected manifestations of the earthquake phenomenon. This awareness is reflected in public policy, enforcement of seismic regulations, and preparedness in both the public and private sector. In the eastern U.S., the public and its decision makers generally do not understand them because of inexperience. Judging seismic risk by rates of seismicity alone (which are low in the east but high in the west) has undoubtedly contributed to the public’s tendency to belittle the seismic loss potential for eastern urban regions.
Let us compare two hypothetical locations, one in California and one in New York City. Assume the location in California does experience, on average, one M = 6 every 10 years, compared to New York once every 1,000 years. This implies a ratio of rates of seismicity of 100:1. Does that mean the ratio of expected losses (when annualized per year) is also 100:1? Most likely not. That ratio may be closer to 10:1, which seems to imply that taking our clues from seismicity alone may lead to an underestimation of the potential seismic risks in the east. Why should this be so?
To check the assertion, let us make a back-of-the-envelope estimate. The expected seismic risk for a given area is defined as the area-integrated product of: seismic hazard (expected shaking level), assets ($ and people), and the assets’ vulnerabilities (that is, their expected fractional loss given a certain hazard – say, shaking level). Thus, if we have a 100 times lower seismicity rate in New York compared to California, which at any given point from a given quake may yield a 2 times higher shaking level in New York compared to California because ground motions in the east are known to differ from those in the west; and if we have a 2 times higher asset density (a modest assumption for Manhattan!), and a 2 times higher vulnerability (again a modest assumption when considering the large stock of unreinforced masonry buildings and aged infrastructure in New York), then our California/New York ratio for annualized loss potential may be on the order of (100/(2x2x2)):1. That implies about a 12:1 risk ratio between the California and New York location, compared to a 100:1 ratio in seismicity rates.
From this example it appears that seismic awareness in the east may be more controlled by the rate of seismicity than by the less well understood risk potential. This misunderstanding is one of the reasons why earthquake awareness and preparedness in the densely populated east is so disproportionally low relative to its seismic loss potential. Rare but potentially catastrophic losses in the east compete in attention with more frequent moderate losses in the west. New York City is the paramount example of a low-probability, high-impact seismic risk, the sort of risk that is hard to insure against, or mobilize public action to reduce the risks.
There are basically two ways to respond. One is to do little and wait until one or more disastrous events occur. Then react to these – albeit disastrous – “windows of opportunity.” That is, pay after the unmitigated facts, rather than attempt to control their outcome. This is a high-stakes approach, considering the evolved state of the economy. The other approach is to invest in mitigation ahead of time, and use scientific knowledge and inference, education, technology transfer, and combine it with a mixture of regulatory and/or economic incentives to implement earthquake preparedness. The National Earthquake Hazard Reduction Program (NEHRP) has attempted the latter while much of the public tends to cling to the former of the two options. Realistic and reliable quantitative loss estimation techniques are essential to evaluate the relative merits of the two approaches.
This paper tries to bring into focus some of the seismological factors which are but one set of variables one needs for quantifying the earthquake loss potential in eastern U.S. urban regions. We use local and global analogs for illustrating possible scenario events in terms of risk. We also highlight some of the few local steps that have been undertaken towards mitigating against the eastern earthquake threat; and discuss priorities for future actions.
NYCEM.org
If today a magnitude 6 earthquake were to occur centered on New York City, what would its effects be? Will the loss be 10 or 100 billion dollars? Will there be 10 or 10,000 fatalities? Will there be 1,000 or 100,000 homeless needing shelter? Can government function, provide assistance, and maintain order?
At this time, no satisfactory answers to these questions are available. A few years ago, rudimentary scenario studies were made for Boston and New York with limited scope and uncertain results. For most eastern cities, including Washington D.C., we know even less about the economic, societal and political impacts from significant earthquakes, whatever their rate of occurrence.
Why do we know so little about such vital public issues? Because the public has been lulled into believing that seriously damaging quakes are so unlikely in the east that in essence we do not need to consider them. We shall examine the validity of this widely held opinion.
Is the public’s earthquake awareness (or lack thereof) controlled by perceived low Seismicity, Seismic Hazard, or Seismic Risk? How do these three seismic features differ from, and relate to each other? In many portions of California, earthquake awareness is refreshed in a major way about once every decade (and in some places even more often) by virtually every person experiencing a damaging event. The occurrence of earthquakes of given magnitudes in time and space, not withstanding their effects, are the manifestations of seismicity. Ground shaking, faulting, landslides or soil liquefaction are the manifestations of seismic hazard. Damage to structures, and loss of life, limb, material assets, business and services are the manifestations of seismic risk. By sheer experience, California’s public understands fairly well these three interconnected manifestations of the earthquake phenomenon. This awareness is reflected in public policy, enforcement of seismic regulations, and preparedness in both the public and private sector. In the eastern U.S., the public and its decision makers generally do not understand them because of inexperience. Judging seismic risk by rates of seismicity alone (which are low in the east but high in the west) has undoubtedly contributed to the public’s tendency to belittle the seismic loss potential for eastern urban regions.
Let us compare two hypothetical locations, one in California and one in New York City. Assume the location in California does experience, on average, one M = 6 every 10 years, compared to New York once every 1,000 years. This implies a ratio of rates of seismicity of 100:1. Does that mean the ratio of expected losses (when annualized per year) is also 100:1? Most likely not. That ratio may be closer to 10:1, which seems to imply that taking our clues from seismicity alone may lead to an underestimation of the potential seismic risks in the east. Why should this be so?
To check the assertion, let us make a back-of-the-envelope estimate. The expected seismic risk for a given area is defined as the area-integrated product of: seismic hazard (expected shaking level), assets ($ and people), and the assets’ vulnerabilities (that is, their expected fractional loss given a certain hazard – say, shaking level). Thus, if we have a 100 times lower seismicity rate in New York compared to California, which at any given point from a given quake may yield a 2 times higher shaking level in New York compared to California because ground motions in the east are known to differ from those in the west; and if we have a 2 times higher asset density (a modest assumption for Manhattan!), and a 2 times higher vulnerability (again a modest assumption when considering the large stock of unreinforced masonry buildings and aged infrastructure in New York), then our California/New York ratio for annualized loss potential may be on the order of (100/(2x2x2)):1. That implies about a 12:1 risk ratio between the California and New York location, compared to a 100:1 ratio in seismicity rates.
From this example it appears that seismic awareness in the east may be more controlled by the rate of seismicity than by the less well understood risk potential. This misunderstanding is one of the reasons why earthquake awareness and preparedness in the densely populated east is so disproportionally low relative to its seismic loss potential. Rare but potentially catastrophic losses in the east compete in attention with more frequent moderate losses in the west. New York City is the paramount example of a low-probability, high-impact seismic risk, the sort of risk that is hard to insure against, or mobilize public action to reduce the risks.
There are basically two ways to respond. One is to do little and wait until one or more disastrous events occur. Then react to these – albeit disastrous – “windows of opportunity.” That is, pay after the unmitigated facts, rather than attempt to control their outcome. This is a high-stakes approach, considering the evolved state of the economy. The other approach is to invest in mitigation ahead of time, and use scientific knowledge and inference, education, technology transfer, and combine it with a mixture of regulatory and/or economic incentives to implement earthquake preparedness. The National Earthquake Hazard Reduction Program (NEHRP) has attempted the latter while much of the public tends to cling to the former of the two options. Realistic and reliable quantitative loss estimation techniques are essential to evaluate the relative merits of the two approaches.
This paper tries to bring into focus some of the seismological factors which are but one set of variables one needs for quantifying the earthquake loss potential in eastern U.S. urban regions. We use local and global analogs for illustrating possible scenario events in terms of risk. We also highlight some of the few local steps that have been undertaken towards mitigating against the eastern earthquake threat; and discuss priorities for future actions.
Wednesday, October 25, 2023
East Coast Still Unprepared For The Sixth Seal (Revelation 6:12)
East Coast Earthquake Preparedness
By By BEN NUCKOLS
Posted: 08/25/2011 8:43 am EDT
WASHINGTON — There were cracks in the Washington Monument and broken capstones at the National Cathedral. In the District of Columbia suburbs, some people stayed in shelters because of structural concerns at their apartment buildings.
A day after the East Coast’s strongest earthquake in 67 years, inspectors assessed the damage and found that most problems were minor. But the shaking raised questions about whether this part of the country, with its older architecture and inexperience with seismic activity, is prepared for a truly powerful quake.
The 5.8 magnitude quake felt from Georgia north to Canada prompted swift inspections of many structures Wednesday, including bridges and nuclear plants. An accurate damage estimate could take weeks, if not longer. And many people will not be covered by insurance.
In a small Virginia city near the epicenter, the entire downtown business district was closed. School was canceled for two weeks to give engineers time to check out cracks in several buildings.
At the 555-foot Washington Monument, inspectors found several cracks in the pyramidion – the section at the top of the obelisk where it begins narrowing to a point.
A 4-foot crack was discovered Tuesday during a visual inspection by helicopter. It cannot be seen from the ground. Late Wednesday, the National Park Service announced that structural engineers had found several additional cracks inside the top of the monument.
Carol Johnson, a park service spokeswoman, could not say how many cracks were found but said three or four of them were “significant.” Two structural engineering firms that specialize in assessing earthquake damage were being brought in to conduct a more thorough inspection on Thursday.
The monument, by far the tallest structure in the nation’s capital, was to remain closed indefinitely, and Johnson said the additional cracks mean repairs are likely to take longer. It has never been damaged by a natural disaster, including earthquakes in Virginia in 1897 and New York in 1944.
Tourists arrived at the monument Wednesday morning only to find out they couldn’t get near it. A temporary fence was erected in a wide circle about 120 feet from the flags that surround its base. Walkways were blocked by metal barriers manned by security guards.
“Is it really closed?” a man asked the clerk at the site’s bookstore.
“It’s really closed,” said the clerk, Erin Nolan. Advance tickets were available for purchase, but she cautioned against buying them because it’s not clear when the monument will open.
“This is pretty much all I’m going to be doing today,” Nolan said.
Tuesday’s quake was centered about 40 miles northwest of Richmond, 90 miles south of Washington and 3.7 miles underground. In the nearby town of Mineral, Va., Michael Leman knew his Main Street Plumbing & Electrical Supply business would need – at best – serious and expensive repairs.
At worst, it could be condemned. The facade had become detached from the rest of the building, and daylight was visible through a 4- to 6-inch gap that opened between the front wall and ceiling.
“We’re definitely going to open back up,” Leman said. “I’ve got people’s jobs to look out for.”
Leman said he is insured, but some property owners might not be so lucky.
The Insurance Information Institute said earthquakes are not covered under standard U.S. homeowners or business insurance policies, although supplemental coverage is usually available.
The institute says coverage for other damage that may result from earthquakes, such as fire and water damage from burst gas or water pipes, is provided by standard homeowners and business insurance policies in most states. Cars and other vehicles with comprehensive insurance would also be protected.
The U.S. Geological Survey classified the quake as Alert Level Orange, the second-most serious category on its four-level scale. Earthquakes in that range lead to estimated losses between $100 million and $1 billion.
In Culpeper, Va., about 35 miles from the epicenter, walls had buckled at the old sanctuary at St. Stephen’s Episcopal Church, which was constructed in 1821 and drew worshippers including Confederate Gens. Robert E. Lee and J.E.B. Stuart. Heavy stone ornaments atop a pillar at the gate were shaken to the ground. A chimney from the old Culpeper Baptist Church built in 1894 also tumbled down.
At the Washington National Cathedral, spokesman Richard Weinberg said the building’s overall structure remains sound and damage was limited to “decorative elements.”
Massive stones atop three of the four spires on the building’s central tower broke off, crashing onto the roof. At least one of the spires is teetering badly, and cracks have appeared in some flying buttresses.
Repairs were expected to cost millions of dollars – an expense not covered by insurance.
“Every single portion of the exterior is carved by hand, so everything broken off is a piece of art,” Weinberg said. “It’s not just the labor, but the artistry of replicating what was once there.”
The building will remain closed as a precaution. Services to dedicate the memorial honoring Rev. Martin Luther King Jr. were moved.
Other major cities along the East Coast that felt the shaking tried to gauge the risk from another quake.
A few hours after briefly evacuating New York City Hall, Mayor Michael Bloomberg said the city’s newer buildings could withstand a more serious earthquake. But, he added, questions remain about the older buildings that are common in a metropolis founded hundreds of years ago.
“We think that the design standards of today are sufficient against any eventuality,” he said. But “there are questions always about some very old buildings. … Fortunately those tend to be low buildings, so there’s not great danger.”
An earthquake similar to the one in Virginia could do billions of dollars of damage if it were centered in New York, said Barbara Nadel, an architect who specializes in securing buildings against natural disasters and terrorism.
The city’s 49-page seismic code requires builders to prepare for significant shifting of the earth. High-rises must be built with certain kinds of bracing, and they must be able to safely sway at least somewhat to accommodate for wind and even shaking from the ground, Nadel said.
Buildings constructed in Boston in recent decades had to follow stringent codes comparable to anything in California, said Vernon Woodworth, an architect and faculty member at the Boston Architectural College. New construction on older structures also must meet tough standards to withstand severe tremors, he said.
It’s a different story with the city’s older buildings. The 18th- and 19th-century structures in Boston’s Back Bay, for instance, were often built on fill, which can liquefy in a strong quake, Woodworth said. Still, there just aren’t many strong quakes in New England.
The last time the Boston area saw a quake as powerful as the one that hit Virginia on Tuesday was in 1755, off Cape Ann, to the north. A repeat of that quake would likely cause deaths, Woodworth said. Still, the quakes are so infrequent that it’s difficult to weigh the risks versus the costs of enacting tougher building standards regionally, he said.
People in several of the affected states won’t have much time to reflect before confronting another potential emergency. Hurricane Irene is approaching the East Coast and could skirt the Mid-Atlantic region by the weekend and make landfall in New England after that.
In North Carolina, officials were inspecting an aging bridge that is a vital evacuation route for people escaping the coastal barrier islands as the storm approaches.
Speaking at an earthquake briefing Wednesday, Washington Mayor Vincent Gray inadvertently mixed up his disasters.
“Everyone knows, obviously, that we had a hurricane,” he said before realizing his mistake.
“Hurricane,” he repeated sheepishly as reporters and staffers burst into laughter. “I’m getting ahead of myself!”
___
Associated Press writers Sam Hananel in Washington; Alex Dominguez in Baltimore; Bob Lewis in Mineral, Va.; Samantha Gross in New York City; and Jay Lindsay in Boston contributed to this report.
By By BEN NUCKOLS
Posted: 08/25/2011 8:43 am EDT
WASHINGTON — There were cracks in the Washington Monument and broken capstones at the National Cathedral. In the District of Columbia suburbs, some people stayed in shelters because of structural concerns at their apartment buildings.
A day after the East Coast’s strongest earthquake in 67 years, inspectors assessed the damage and found that most problems were minor. But the shaking raised questions about whether this part of the country, with its older architecture and inexperience with seismic activity, is prepared for a truly powerful quake.
The 5.8 magnitude quake felt from Georgia north to Canada prompted swift inspections of many structures Wednesday, including bridges and nuclear plants. An accurate damage estimate could take weeks, if not longer. And many people will not be covered by insurance.
In a small Virginia city near the epicenter, the entire downtown business district was closed. School was canceled for two weeks to give engineers time to check out cracks in several buildings.
At the 555-foot Washington Monument, inspectors found several cracks in the pyramidion – the section at the top of the obelisk where it begins narrowing to a point.
A 4-foot crack was discovered Tuesday during a visual inspection by helicopter. It cannot be seen from the ground. Late Wednesday, the National Park Service announced that structural engineers had found several additional cracks inside the top of the monument.
Carol Johnson, a park service spokeswoman, could not say how many cracks were found but said three or four of them were “significant.” Two structural engineering firms that specialize in assessing earthquake damage were being brought in to conduct a more thorough inspection on Thursday.
The monument, by far the tallest structure in the nation’s capital, was to remain closed indefinitely, and Johnson said the additional cracks mean repairs are likely to take longer. It has never been damaged by a natural disaster, including earthquakes in Virginia in 1897 and New York in 1944.
Tourists arrived at the monument Wednesday morning only to find out they couldn’t get near it. A temporary fence was erected in a wide circle about 120 feet from the flags that surround its base. Walkways were blocked by metal barriers manned by security guards.
“Is it really closed?” a man asked the clerk at the site’s bookstore.
“It’s really closed,” said the clerk, Erin Nolan. Advance tickets were available for purchase, but she cautioned against buying them because it’s not clear when the monument will open.
“This is pretty much all I’m going to be doing today,” Nolan said.
Tuesday’s quake was centered about 40 miles northwest of Richmond, 90 miles south of Washington and 3.7 miles underground. In the nearby town of Mineral, Va., Michael Leman knew his Main Street Plumbing & Electrical Supply business would need – at best – serious and expensive repairs.
At worst, it could be condemned. The facade had become detached from the rest of the building, and daylight was visible through a 4- to 6-inch gap that opened between the front wall and ceiling.
“We’re definitely going to open back up,” Leman said. “I’ve got people’s jobs to look out for.”
Leman said he is insured, but some property owners might not be so lucky.
The Insurance Information Institute said earthquakes are not covered under standard U.S. homeowners or business insurance policies, although supplemental coverage is usually available.
The institute says coverage for other damage that may result from earthquakes, such as fire and water damage from burst gas or water pipes, is provided by standard homeowners and business insurance policies in most states. Cars and other vehicles with comprehensive insurance would also be protected.
The U.S. Geological Survey classified the quake as Alert Level Orange, the second-most serious category on its four-level scale. Earthquakes in that range lead to estimated losses between $100 million and $1 billion.
In Culpeper, Va., about 35 miles from the epicenter, walls had buckled at the old sanctuary at St. Stephen’s Episcopal Church, which was constructed in 1821 and drew worshippers including Confederate Gens. Robert E. Lee and J.E.B. Stuart. Heavy stone ornaments atop a pillar at the gate were shaken to the ground. A chimney from the old Culpeper Baptist Church built in 1894 also tumbled down.
At the Washington National Cathedral, spokesman Richard Weinberg said the building’s overall structure remains sound and damage was limited to “decorative elements.”
Massive stones atop three of the four spires on the building’s central tower broke off, crashing onto the roof. At least one of the spires is teetering badly, and cracks have appeared in some flying buttresses.
Repairs were expected to cost millions of dollars – an expense not covered by insurance.
“Every single portion of the exterior is carved by hand, so everything broken off is a piece of art,” Weinberg said. “It’s not just the labor, but the artistry of replicating what was once there.”
The building will remain closed as a precaution. Services to dedicate the memorial honoring Rev. Martin Luther King Jr. were moved.
Other major cities along the East Coast that felt the shaking tried to gauge the risk from another quake.
A few hours after briefly evacuating New York City Hall, Mayor Michael Bloomberg said the city’s newer buildings could withstand a more serious earthquake. But, he added, questions remain about the older buildings that are common in a metropolis founded hundreds of years ago.
“We think that the design standards of today are sufficient against any eventuality,” he said. But “there are questions always about some very old buildings. … Fortunately those tend to be low buildings, so there’s not great danger.”
An earthquake similar to the one in Virginia could do billions of dollars of damage if it were centered in New York, said Barbara Nadel, an architect who specializes in securing buildings against natural disasters and terrorism.
The city’s 49-page seismic code requires builders to prepare for significant shifting of the earth. High-rises must be built with certain kinds of bracing, and they must be able to safely sway at least somewhat to accommodate for wind and even shaking from the ground, Nadel said.
Buildings constructed in Boston in recent decades had to follow stringent codes comparable to anything in California, said Vernon Woodworth, an architect and faculty member at the Boston Architectural College. New construction on older structures also must meet tough standards to withstand severe tremors, he said.
It’s a different story with the city’s older buildings. The 18th- and 19th-century structures in Boston’s Back Bay, for instance, were often built on fill, which can liquefy in a strong quake, Woodworth said. Still, there just aren’t many strong quakes in New England.
The last time the Boston area saw a quake as powerful as the one that hit Virginia on Tuesday was in 1755, off Cape Ann, to the north. A repeat of that quake would likely cause deaths, Woodworth said. Still, the quakes are so infrequent that it’s difficult to weigh the risks versus the costs of enacting tougher building standards regionally, he said.
People in several of the affected states won’t have much time to reflect before confronting another potential emergency. Hurricane Irene is approaching the East Coast and could skirt the Mid-Atlantic region by the weekend and make landfall in New England after that.
In North Carolina, officials were inspecting an aging bridge that is a vital evacuation route for people escaping the coastal barrier islands as the storm approaches.
Speaking at an earthquake briefing Wednesday, Washington Mayor Vincent Gray inadvertently mixed up his disasters.
“Everyone knows, obviously, that we had a hurricane,” he said before realizing his mistake.
“Hurricane,” he repeated sheepishly as reporters and staffers burst into laughter. “I’m getting ahead of myself!”
___
Associated Press writers Sam Hananel in Washington; Alex Dominguez in Baltimore; Bob Lewis in Mineral, Va.; Samantha Gross in New York City; and Jay Lindsay in Boston contributed to this report.
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
The Next Major Quake: The Sixth Seal of NYC
New York is OVERDUE an earthquake from a ‚brittle grid‘ of faults under the city, expert warns
- New York City last experienced a M5 or higher earthquake in 1884, experts say
- It’s thought that these earthquakes occur on a roughly 150-year periodicity
- Based on this, some say the city could be overdue for the next major quake
Published: 15:50 EDT, 1 September 2017 | Updated: 12:00 EDT, 2 September 2017
When you think of the impending earthquake risk in the United States, it’s likely California or the Pacific Northwest comes to mind.
But, experts warn a system of faults making up a ‘brittle grid’ beneath New York City could also be loading up for a massive temblor.
The city has been hit by major quakes in the past, along what’s thought to be roughly 150-year intervals, and researchers investigating these faults now say the region could be overdue for the next event.
Experts warn a system of faults making up a ‘brittle grid’ beneath New York City could also be loading up for a massive temblor. The city has been hit by major quakes in the past, along what’s thought to be roughly 150-year intervals. A stock image is pictured
THE ‚CONEY ISLAND EARTHQUAKE‘
On August 10, 1884, New York was struck by a magnitude 5.5 earthquake with an epicentre located in Brooklyn.
While there was little damage and few injuries reported, anecdotal accounts of the event reveal the frightening effects of the quake.
One newspaper even reported that it caused someone to die from fright.
According to a New York Times report following the quake, massive buildings, including the Post Office swayed back and forth.
And, police said they felt the Brooklyn Bridge swaying ‘as if struck by a hurricane,’ according to an adaptation of Kathryn Miles’ book Quakeland: On the Road to America’s Next Devastating Earthquake.
The rumbles were felt across a 70,000-square-mile area, causing broken windows and cracked walls as far as Pennsylvania and Connecticut.
The city hasn’t experienced an earthquake this strong since.
According to geologist Dr Charles Merguerian, who has walked the entirety of Manhattan to assess its seismicity, there are a slew of faults running through New York, reports author Kathryn Miles in an adaptation of her new book Quakeland: On the Road to America’s Next Devastating Earthquake.
One such fault passes through 125th street, otherwise known as the Manhattanville Fault.
While there have been smaller quakes in New York’s recent past, including a magnitude 2.6 that struck in October 2001, it’s been decades since the last major tremor of M 5 or more.
And, most worryingly, the expert says there’s no way to predict exactly when a quake will strike.
‘That’s a question you really can’t answer,’ Merguerian has explained in the past.
‘All we can do is look at the record, and the record is that there was a relatively large earthquake here in the city in 1737, and in 1884, and that periodicity is about 150 year heat cycle.
‘So you have 1737, 1884, 20- and, we’re getting there. But statistics can lie.
‘An earthquake could happen any day, or it couldn’t happen for 100 years, and you just don’t know, there’s no way to predict.’
Compared the other parts of the United States, the risk of an earthquake in New York may not seem as pressing.
But, experts explain that a quake could happen anywhere.
According to geologist Dr Charles Merguerian, there are a slew of faults running through NY. One is the Ramapo Fault
‘All states have some potential for damaging earthquake shaking,’ according to the US Geological Survey.
‘Hazard is especially high along the west coast but also in the intermountain west, and in parts of the central and eastern US.’
A recent assessment by the USGS determined that the earthquake hazard along the East Coast may previously have been underestimated.
‘The eastern U.S. has the potential for larger and more damaging earthquakes than considered in previous maps and assessments,’ the USGS report explained.
The experts point to a recent example – the magnitude 5.8 earthquake that hit Virginia in 2011, which was among the largest to occur on the east coast in the last century.
This event suggests the area could be subjected to even larger earthquakes, even raising the risk for Charleston, SC.
It also indicates that New York City may be at higher risk than once thought.
A recent assessment by the USGS determined that the earthquake hazard along the East Coast may previously have been underestimated. The varying risks around the US can be seen above, with New York City in the mid-range (yellow).
Monday, October 23, 2023
Quakeland: On the Road to America’s Next Devastating Earthquake: Revelation 6

Quakeland: On the Road to America’s Next Devastating Earthquake
Roger BilhamQuakeland: New York and the Sixth Seal (Revelation 6:12)
Given recent seismic activity — political as well as geological — it’s perhaps unsurprising that two books on earthquakes have arrived this season. One is as elegant as the score of a Beethoven symphony; the other resembles a diary of conversations overheard during a rock concert. Both are interesting, and both relate recent history to a shaky future.
Journalist Kathryn Miles’s Quakeland is a litany of bad things that happen when you provoke Earth to release its invisible but ubiquitous store of seismic-strain energy, either by removing fluids (oil, water, gas) or by adding them in copious quantities (when extracting shale gas in hydraulic fracturing, also known as fracking, or when injecting contaminated water or building reservoirs). To complete the picture, she describes at length the bad things that happen during unprovoked natural earthquakes. As its subtitle hints, the book takes the form of a road trip to visit seismic disasters both past and potential, and seismologists and earthquake engineers who have first-hand knowledge of them. Their colourful personalities, opinions and prejudices tell a story of scientific discovery and engineering remedy.
Miles poses some important societal questions. Aside from human intervention potentially triggering a really damaging earthquake, what is it actually like to live in neighbourhoods jolted daily by magnitude 1–3 earthquakes, or the occasional magnitude 5? Are these bumps in the night acceptable? And how can industries that perturb the highly stressed rocks beneath our feet deny obvious cause and effect? In 2015, the Oklahoma Geological Survey conceded that a quadrupling of the rate of magnitude-3 or more earthquakes in recent years, coinciding with a rise in fracking, was unlikely to represent a natural process. Miles does not take sides, but it’s difficult for the reader not to.
She visits New York City, marvelling at subway tunnels and unreinforced masonry almost certainly scheduled for destruction by the next moderate earthquake in the vicinity. She considers the perils of nuclear-waste storage in Nevada and Texas, and ponders the risks to Idaho miners of rock bursts — spontaneous fracture of the working face when the restraints of many million years of confinement are mined away. She contemplates the ups and downs of the Yellowstone Caldera — North America’s very own mid-continent supervolcano — and its magnificently uncertain future. Miles also touches on geothermal power plants in southern California’s Salton Sea and elsewhere; the vast US network of crumbling bridges, dams and oil-storage farms; and the magnitude 7–9 earthquakes that could hit California and the Cascadia coastline of Oregon and Washington state this century. Amid all this doom, a new elementary school on the coast near Westport, Washington, vulnerable to inbound tsunamis, is offered as a note of optimism. With foresight and much persuasion from its head teacher, it was engineered to become an elevated safe haven.
Miles briefly discusses earthquake prediction and the perils of getting it wrong (embarrassment in New Madrid, Missouri, where a quake was predicted but never materialized; prison in L’Aquila, Italy, where scientists failed to foresee a devastating seismic event) and the successes of early-warning systems, with which electronic alerts can be issued ahead of damaging seismic waves. Yes, it’s a lot to digest, but most of the book obeys the laws of physics, and it is a engaging read. One just can’t help wishing that Miles’s road trips had taken her somewhere that wasn’t a disaster waiting to happen.
Catastrophic damage in Anchorage, Alaska, in 1964, caused by the second-largest earthquake in the global instrumental record.
In The Great Quake, journalist Henry Fountain provides us with a forthright and timely reminder of the startling historical consequences of North America’s largest known earthquake, which more than half a century ago devastated southern Alaska. With its epicentre in Prince William Sound, the 1964 quake reached magnitude 9.2, the second largest in the global instrumental record. It released more energy than either the 2004 Sumatra–Andaman earthquake or the 2011 Tohoku earthquake off Japan; and it generated almost as many pages of scientific commentary and description as aftershocks. Yet it has been forgotten by many.
The quake was scientifically important because it occurred at a time when plate tectonics was in transition from hypothesis to theory. Fountain expertly traces the theory’s historical development, and how the Alaska earthquake was pivotal in nailing down one of the most important predictions. The earthquake caused a fjordland region larger than England to subside, and a similarly huge region of islands offshore to rise by many metres; but its scientific implications were not obvious at the time. Eminent seismologists thought that a vertical fault had slipped, drowning forests and coastlines to its north and raising beaches and islands to its south. But this kind of fault should have reached the surface, and extended deep into Earth’s mantle. There was no geological evidence of a monster surface fault separating these two regions, nor any evidence for excessively deep aftershocks. The landslides and liquefied soils that collapsed houses, and the tsunami that severely damaged ports and infrastructure, offered no clues to the cause.
“Previous earthquakes provide clear guidance about present-day vulnerability.” The hero of The Great Quake is the geologist George Plafker, who painstakingly mapped the height reached by barnacles lifted out of the intertidal zone along shorelines raised by the earthquake, and documented the depths of drowned forests. He deduced that the region of subsidence was the surface manifestation of previously compressed rocks springing apart, driving parts of Alaska up and southwards over the Pacific Plate. His finding confirmed a prediction of plate tectonics, that the leading edge of the Pacific Plate plunged beneath the southern edge of Alaska along a gently dipping thrust fault. That observation, once fully appreciated, was applauded by the geophysics community.
Fountain tells this story through the testimony of survivors, engineers and scientists, interweaving it with the fascinating history of Alaska, from early discovery by Europeans to purchase from Russia by the United States in 1867, and its recent development. Were the quake to occur now, it is not difficult to envisage that with increased infrastructure and larger populations, the death toll and price tag would be two orders of magnitude larger than the 139 fatalities and US$300-million economic cost recorded in 1964.
What is clear from these two books is that seismicity on the North American continent is guaranteed to deliver surprises, along with unprecedented economic and human losses. Previous earthquakes provide clear guidance about the present-day vulnerability of US infrastructure and populations. Engineers and seismologists know how to mitigate the effects of future earthquakes (and, in mid-continent, would advise against the reckless injection of waste fluids known to trigger earthquakes). It is merely a matter of persuading city planners and politicians that if they are tempted to ignore the certainty of the continent’s seismic past, they should err on the side of caution when considering its seismic future.
Saturday, October 21, 2023
New York Subways at the Sixth Seal (Revelation 6)
How vulnerable are NYC’s underwater subway tunnels to flooding?
New York City is full of peculiar phenomena—rickety fire escapes; 100-year-old subway tunnels; air conditioners propped perilously into window frames—that can strike fear into the heart of even the toughest city denizen. But should they? Every month, writer Ashley Fetters will be exploring—and debunking—these New York-specific fears, letting you know what you should actually worry about, and what anxieties you can simply let slip away.
The 25-minute subway commute from Crown Heights to the Financial District on the 2/3 line is, in my experience, a surprisingly peaceful start to the workday—save for one 3,100-foot stretch between the Clark Street and Wall Street stations, where for three minutes I sit wondering what the probability is that I will soon die a torturous, claustrophobic drowning death right here in this subway car.
The Clark Street Tunnel, opened in 1916, is one of approximately a dozen tunnels that escort MTA passengers from one borough to the next underwater—and just about all of them, with the exception of the 1989 addition of the 63rd Street F train tunnel, were constructed between 1900 and 1936.
Each day, thousands of New Yorkers venture across the East River and back again through these tubes buried deep in the riverbed, some of which are nearing or even past their 100th birthdays. Are they wrong to ponder their own mortality while picturing one of these watery catacombs suddenly springing a leak?
Mostly yes, they are, says Michael Horodniceanu, the former president of MTA Capital Construction and current principal of Urban Advisory Group. First, it’s important to remember that the subway tunnel is built under the riverbed, not just in the river—so what immediately surrounds the tunnel isn’t water but some 25 feet of soil. “There’s a lot of dirt on top of it,” Horodniceanu says. “It’s well into the bed of the bottom of the channel.”
And second, as Angus Kress Gillespie, author of Crossing Under the Hudson: The Story of the Holland and Lincoln Tunnels, points out, New York’s underwater subway tunnels are designed to withstand some leaking. And withstand it they do: Pumps placed below the floor of the tunnel, he says, are always running, always diverting water seepage into the sewers. (Horodniceanu says the amount of water these pumps divert into the sewer system each day numbers in the thousands of gallons.)
Additionally, MTA crews routinely repair the grouting and caulking, and often inject a substance into the walls that creates a waterproof membrane outside the tunnel—which keeps water out of the tunnel and relieves any water pressure acting on its walls. New tunnels, Horodniceanu points out, are even built with an outside waterproofing membrane that works like an umbrella: Water goes around it, it falls to the sides, and then it gets channeled into a pumping station and pumped out.
Of course, the classic New York nightmare scenario isn’t just a cute little trickle finding its way in. The anxiety daydream usually involves something sinister, or seismic. The good news, however, is that while an earthquake or explosion would indeed be bad for many reasons, it likely wouldn’t result in the frantic flooding horror scene that plays out in some commuters’ imaginations.
The Montague Tube, which sustained severe damage during Hurricane Sandy.
MTA New York City Transit / Marc A. Hermann
Horodniceanu assures me that tunnels built more recently are “built to withstand a seismic event.” The older tunnels, however—like, um, the Clark Street Tunnel—“were not seismically retrofitted, let me put it that way,” Horodniceanu says. “But the way they were built is in such a way that I do not believe an earthquake would affect them.” They aren’t deep enough in the ground, anyway, he says, to be too intensely affected by a seismic event. (The MTA did not respond to a request for comment.)
One of the only real threats to tunnel infrastructure, Horodniceanu adds, is extreme weather. Hurricane Sandy, for example, caused flooding in the tunnels, which “created problems with the infrastructure.” He continues, “The tunnels have to be rebuilt as a result of saltwater corroding the infrastructure.”
Still, he points out, hurricanes don’t exactly happen with no warning. So while Hurricane Sandy did cause major trauma to the tunnels, train traffic could be stopped with ample time to keep passengers out of harm’s way. In 2012, Governor Andrew Cuomo directed all the MTA’s mass transit services to shut down at 7 p.m. the night before Hurricane Sandy was expected to hit New York City.
And Gillespie, for his part, doubts even an explosion would result in sudden, dangerous flooding. A subway tunnel is not a closed system, he points out; it’s like a pipe that’s open at both ends. “The force of a blast would go forwards and backwards out the exit,” he says.
So the subway-train version of that terrifying Holland Tunnel flood scene in Sylvester Stallone’s Daylight is … unrealistic, right?
“Yeah,” Gillespie laughs. “Yeah. It is.”
Got a weird New York anxiety that you want explored? E-mail tips@curbed.com, and we may include it in a future column.
Friday, October 20, 2023
The Sixth Seal Long Overdue (Revelation 6)
The Big One Awaits
By MARGO NASH
Published: March 25, 2001
Alexander Gates, a geology professor at Rutgers-Newark, is co-author of “The Encyclopedia of Earthquakes and Volcanoes,“ which will be published by Facts on File in July. He has been leading a four-year effort to remap an area known as the Sloatsburg Quadrangle, a 5-by-7-mile tract near Mahwah that crosses into New York State. The Ramapo Fault, which runs through it, was responsible for a big earthquake in 1884, and Dr. Gates warns that a recurrence is overdue. He recently talked about his findings.
Q. What have you found?
A. We’re basically looking at a lot more rock, and we’re looking at the fracturing and jointing in the bedrock and putting it on the maps. Any break in the rock is a fracture. If it has movement, then it’s a fault. There are a lot of faults that are offshoots of the Ramapo. Basically when there are faults, it means you had an earthquake that made it. So there was a lot of earthquake activity to produce these features. We are basically not in a period of earthquake activity along the Ramapo Fault now, but we can see that about six or seven times in history, about 250 million years ago, it had major earthquake activity. And because it’s such a fundamental zone of weakness, anytime anything happens, the Ramapo Fault goes.
Q. Where is the Ramapo Fault?
A. The fault line is in western New Jersey and goes through a good chunk of the state, all the way down to Flemington. It goes right along where they put in the new 287. It continues northeast across the Hudson River right under the Indian Point power plant up into Westchester County. There are a lot of earthquakes rumbling around it every year, but not a big one for a while.
Q. Did you find anything that surprised you?
A. I found a lot of faults, splays that offshoot from the Ramapo that go 5 to 10 miles away from the fault. I have looked at the Ramapo Fault in other places too. I have seen splays 5 to 10 miles up into the Hudson Highlands. And you can see them right along the roadsides on 287. There’s been a lot of damage to those rocks, and obviously it was produced by fault activities. All of these faults have earthquake potential.
Q. Describe the 1884 earthquake.
A. It was in the northern part of the state near the Sloatsburg area. They didn’t have precise ways of describing the location then. There was lots of damage. Chimneys toppled over. But in 1884, it was a farming community, and there were not many people to be injured. Nobody appears to have written an account of the numbers who were injured.
Q. What lessons we can learn from previous earthquakes?
A. In 1960, the city of Agadir in Morocco had a 6.2 earthquake that killed 12,000 people, a third of the population, and injured a third more. I think it was because the city was unprepared.There had been an earthquake in the area 200 years before. But people discounted the possibility of a recurrence. Here in New Jersey, we should not make the same mistake. We should not forget that we had a 5.4 earthquake 117 years ago. The recurrence interval for an earthquake of that magnitude is every 50 years, and we are overdue. The Agadir was a 6.2, and a 5.4 to a 6.2 isn’t that big a jump.
Q. What are the dangers of a quake that size?
A. When you’re in a flat area in a wooden house it’s obviously not as dangerous, although it could cut off a gas line that could explode. There’s a real problem with infrastructure that is crumbling, like the bridges with crumbling cement. There’s a real danger we could wind up with our water supplies and electricity cut off if a sizable earthquake goes off. The best thing is to have regular upkeep and keep up new building codes. The new buildings will be O.K. But there is a sense of complacency.
MARGO NASH
Thursday, October 19, 2023
History Says Expect The Sixth Seal In New York (Revelation 6:12)

History Says New York Is Earthquake Prone
According to the New York Daily News, Lynn Skyes, lead author of a recent study by seismologists at the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory adds that a magnitude-6 quake hits the area about every 670 years, and magnitude-7 every 3,400 years.
A 5.2-magnitude quake shook New York City in 1737 and another of the same severity hit in 1884.
Tremors were felt from Maine to Virginia.
There are several fault lines in the metro area, including one along Manhattan’s 125th St. – which may have generated two small tremors in 1981 and may have been the source of the major 1737 earthquake, says Armbruster.
“The problem here comes from many subtle faults,” explained Skyes after the study was published.
He adds: “We now see there is earthquake activity on them. Each one is small, but when you add them up, they are probably more dangerous than we thought.”
“Considering population density and the condition of the region’s infrastructure and building stock, it is clear that even a moderate earthquake would have considerable consequences in terms of public safety and economic impact,” says the New York City Area Consortium for Earthquake Loss Mitigation on its website.
Armbruster says a 5.0-magnitude earthquake today likely would result in casualties and hundreds of millions of dollars in damage.
“I would expect some people to be killed,” he notes.
The scope and scale of damage would multiply exponentially with each additional tick on the Richter scale. (ANI)
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)





