Earthquakes May Endanger New York More Than Thought, Says Study
A study by a group of prominent seismologists suggests that a pattern of subtle but active faults makes the risk of earthquakes to the New York City area substantially greater than formerly believed. Among other things, they say that the controversial Indian Point nuclear power plants, 24 miles north of the city, sit astride the previously unidentified intersection of two active seismic zones. The paper appears in the current issue of the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America.
Many faults and a few mostly modest quakes have long been known around New York City, but the research casts them in a new light. The scientists say the insight comes from sophisticated analysis of past quakes, plus 34 years of new data on tremors, most of them perceptible only by modern seismic instruments. The evidence charts unseen but potentially powerful structures whose layout and dynamics are only now coming clearer, say the scientists. All are based at Columbia University’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, which runs the network of seismometers that monitors most of the northeastern United States.
Lead author Lynn R. Sykes said the data show that large quakes are infrequent around New Yorkcompared to more active areas like California and Japan, but that the risk is high, because of the overwhelming concentration of people and infrastructure. “The research raises the perception both of how common these events are, and, specifically, where they may occur,” he said. “It’s an extremely populated area with very large assets.” Sykes, who has studied the region for four decades, is known for his early role in establishing the global theory of plate tectonics.
The authors compiled a catalog of all 383 known earthquakes from 1677 to 2007 in a 15,000-square-mile area around New York City. Coauthor John Armbruster estimated sizes and locations of dozens of events before 1930 by combing newspaper accounts and other records. The researchers say magnitude 5 quakes—strong enough to cause damage–occurred in 1737, 1783 and 1884. There was little settlement around to be hurt by the first two quakes, whose locations are vague due to a lack of good accounts; but the last, thought to be centered under the seabed somewhere between Brooklyn and Sandy Hook, toppled chimneys across the city and New Jersey, and panicked bathers at Coney Island. Based on this, the researchers say such quakes should be routinely expected, on average, about every 100 years. “Today, with so many more buildings and people, a magnitude 5 centered below the city would be extremely attention-getting,” said Armbruster. “We’d see billions in damage, with some brick buildings falling. People would probably be killed.”
Starting in the early 1970s Lamont began collecting data on quakes from dozens of newly deployed seismometers; these have revealed further potential, including distinct zones where earthquakes concentrate, and where larger ones could come. The Lamont network, now led by coauthor Won-Young Kim, has located hundreds of small events, including a magnitude 3 every few years, which can be felt by people at the surface, but is unlikely to cause damage. These small quakes tend to cluster along a series of small, old faults in harder rocks across the region. Many of the faults were discovered decades ago when subways, water tunnels and other excavations intersected them, but conventional wisdom said they were inactive remnants of continental collisions and rifting hundreds of millions of years ago. The results clearly show that they are active, and quite capable of generating damaging quakes, said Sykes.
One major previously known feature, the Ramapo Seismic Zone, runs from eastern Pennsylvania to the mid-Hudson Valley, passing within a mile or two northwest of Indian Point. The researchers found that this system is not so much a single fracture as a braid of smaller ones, where quakes emanate from a set of still ill-defined faults. East and south of the Ramapo zone—and possibly more significant in terms of hazard–is a set of nearly parallel northwest-southeast faults. These include Manhattan’s 125th Street fault, which seems to have generated two small 1981 quakes, and could have been the source of the big 1737 quake; the Dyckman Street fault, which carried a magnitude 2 in 1989; the Mosholu Parkway fault; and the Dobbs Ferry fault in suburban Westchester, which generated the largest recent shock, a surprising magnitude 4.1, in 1985. Fortunately, it did no damage. Given the pattern, Sykes says the big 1884 quake may have hit on a yet-undetected member of this parallel family further south.
The researchers say that frequent small quakes occur in predictable ratios to larger ones, and so can be used to project a rough time scale for damaging events. Based on the lengths of the faults, the detected tremors, and calculations of how stresses build in the crust, the researchers say that magnitude 6 quakes, or even 7—respectively 10 and 100 times bigger than magnitude 5–are quite possible on the active faults they describe. They calculate that magnitude 6 quakes take place in the area about every 670 years, and sevens, every 3,400 years. The corresponding probabilities of occurrence in any 50-year period would be 7% and 1.5%. After less specific hints of these possibilities appeared in previous research, a 2003 analysis by The New York City Area Consortium for Earthquake Loss Mitigation put the cost of quakes this size in the metro New York area at $39 billion to $197 billion. A separate 2001 analysis for northern New Jersey’s Bergen County estimates that a magnitude 7 would destroy 14,000 buildings and damage 180,000 in that area alone. The researchers point out that no one knows when the last such events occurred, and say no one can predict when they next might come.
“We need to step backward from the simple old model, where you worry about one large, obvious fault, like they do in California,” said coauthor Leonardo Seeber. “The problem here comes from many subtle faults. We now see there is earthquake activity on them. Each one is small, but when you add them up, they are probably more dangerous than we thought. We need to take a very close look.” Seeber says that because the faults are mostly invisible at the surface and move infrequently, a big quake could easily hit one not yet identified. “The probability is not zero, and the damage could be great,” he said. “It could be like something out of a Greek myth.”
The researchers found concrete evidence for one significant previously unknown structure: an active seismic zone running at least 25 miles from Stamford, Conn., to the Hudson Valley town of Peekskill, N.Y., where it passes less than a mile north of the Indian Point nuclear power plant. The Stamford-Peekskill line stands out sharply on the researchers’ earthquake map, with small events clustered along its length, and to its immediate southwest. Just to the north, there are no quakes, indicating that it represents some kind of underground boundary. It is parallel to the other faults beginning at 125th Street, so the researchers believe it is a fault in the same family. Like the others, they say it is probably capable of producing at least a magnitude 6 quake. Furthermore, a mile or so on, it intersects the Ramapo seismic zone.
Sykes said the existence of the Stamford-Peekskill line had been suggested before, because the Hudson takes a sudden unexplained bend just ot the north of Indian Point, and definite traces of an old fault can be along the north side of the bend. The seismic evidence confirms it, he said. “Indian Point is situated at the intersection of the two most striking linear features marking the seismicity and also in the midst of a large population that is at risk in case of an accident,” says the paper. “This is clearly one of the least favorable sites in our study area from an earthquake hazard and risk perspective.”
The findings comes at a time when Entergy, the owner of Indian Point, is trying to relicense the two operating plants for an additional 20 years—a move being fought by surrounding communities and the New York State Attorney General. Last fall the attorney general, alerted to the then-unpublished Lamont data, told a Nuclear Regulatory Commission panel in a filing: “New data developed in the last 20 years disclose a substantially higher likelihood of significant earthquake activity in the vicinity of [Indian Point] that could exceed the earthquake design for the facility.” The state alleges that Entergy has not presented new data on earthquakes past 1979. However, in a little-noticed decision this July 31, the panel rejected the argument on procedural grounds. A source at the attorney general’s office said the state is considering its options.
The characteristics of New York’s geology and human footprint may increase the problem. Unlike in California, many New York quakes occur near the surface—in the upper mile or so—and they occur not in the broken-up, more malleable formations common where quakes are frequent, but rather in the extremely hard, rigid rocks underlying Manhattan and much of the lower Hudson Valley. Such rocks can build large stresses, then suddenly and efficiently transmit energy over long distances. “It’s like putting a hard rock in a vise,” said Seeber. “Nothing happens for a while. Then it goes with a bang.” Earthquake-resistant building codes were not introduced to New York City until 1995, and are not in effect at all in many other communities. Sinuous skyscrapers and bridges might get by with minimal damage, said Sykes, but many older, unreinforced three- to six-story brick buildings could crumble.
Art Lerner-Lam, associate director of Lamont for seismology, geology and tectonophysics, pointed out that the region’s major highways including the New York State Thruway, commuter and long-distance rail lines, and the main gas, oil and power transmission lines all cross the parallel active faults, making them particularly vulnerable to being cut. Lerner-Lam, who was not involved in the research, said that the identification of the seismic line near Indian Point “is a major substantiation of a feature that bears on the long-term earthquake risk of the northeastern United States.” He called for policymakers to develop more information on the region’s vulnerability, to take a closer look at land use and development, and to make investments to strengthen critical infrastructure.
“This is a landmark study in many ways,” said Lerner-Lam. “It gives us the best possible evidence that we have an earthquake hazard here that should be a factor in any planning decision. It crystallizes the argument that this hazard is not random. There is a structure to the location and timing of the earthquakes. This enables us to contemplate risk in an entirely different way. And since we are able to do that, we should be required to do that.”
New York Earthquake Briefs and Quotes:
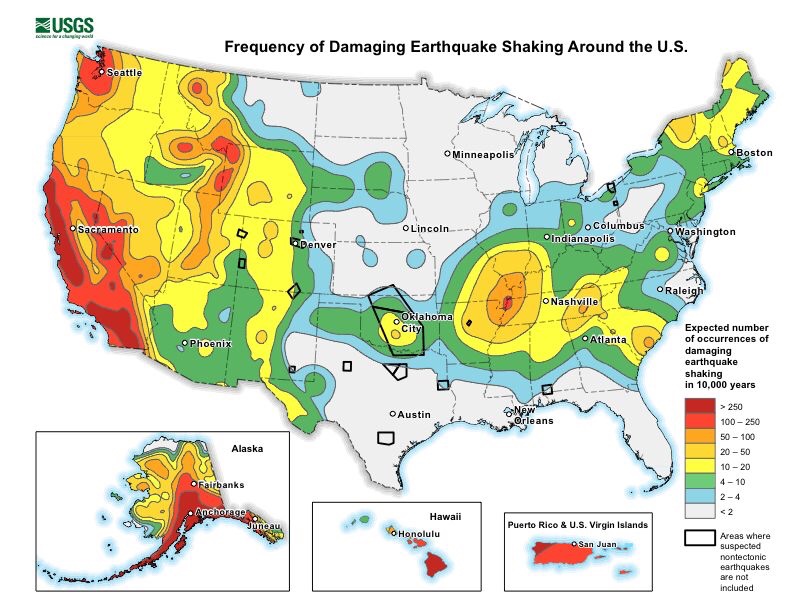
Existing U.S. Geological Survey seismic hazard maps show New York City as facing more hazard than many other eastern U.S. areas. Three areas are somewhat more active—northernmost New York State, New Hampshire and South Carolina—but they have much lower populations and fewer structures. The wider forces at work include pressure exerted from continuing expansion of the mid-Atlantic Ridge thousands of miles to the east; slow westward migration of the North American continent; and the area’s intricate labyrinth of old faults, sutures and zones of weakness caused by past collisions and rifting.
Due to New York’s past history, population density and fragile, interdependent infrastructure, a 2001 analysis by the Federal Emergency Management Agency ranks it the 11th most at-risk U.S. city for earthquake damage. Among those ahead: Los Angeles, San Francisco, Seattle and Portland. Behind: Salt Lake City, Sacramento, Anchorage.
New York’s first seismic station was set up at Fordham University in the 1920s. Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, in Palisades, N.Y., has operated stations since 1949, and now coordinates a network of about 40.
Dozens of small quakes have been felt in the New York area. A Jan. 17, 2001 magnitude 2.4, centered in the Upper East Side—the first ever detected in Manhattan itself–may have originated on the 125th Street fault. Some people thought it was an explosion, but no one was harmed.
The most recent felt quake, a magnitude 2.1 on July 28, 2008, was centered near Milford, N.J. Houses shook and a woman at St. Edward’s Church said she felt the building rise up under her feet—but no damage was done.
Questions about the seismic safety of the Indian Point nuclear power plant, which lies amid a metropolitan area of more than 20 million people, were raised in previous scientific papers in 1978 and 1985.
Because the hard rocks under much of New York can build up a lot strain before breaking, researchers believe that modest faults as short as 1 to 10 kilometers can cause magnitude 5 or 6 quakes.
In general, magnitude 3 quakes occur about 10 times more often than magnitude fours; 100 times more than magnitude fives; and so on. This principle is called the Gutenberg-Richter relationship.