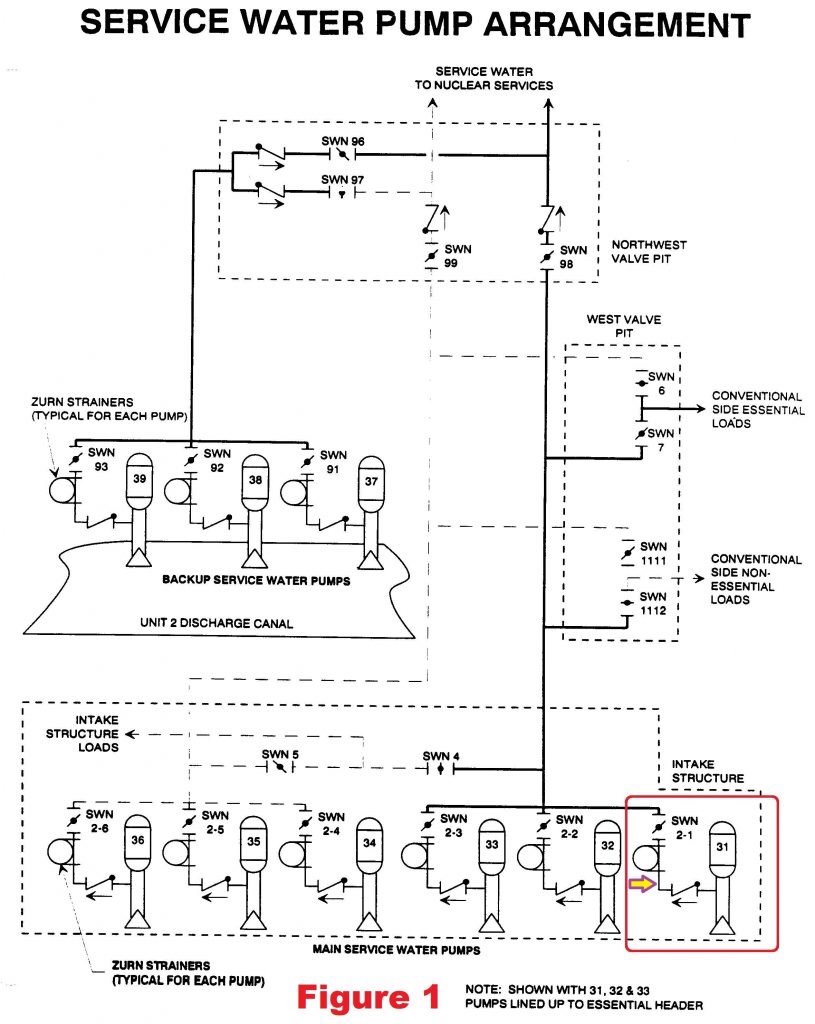

Support from UCS members make work like this possible. Will you join us? Help UCS advance independent science for a healthy environment and a safer world.he Hudson River. The six SW pumps are arranged in two sets of three pumps. Figure 1 shows SW pumps 31, 32, and 33 aligned to provide water drawn from the Hudson River to essential (i.e, safety and emergency) components within Unit 3. SW pumps 34, 35, and 36 are aligned to provide cooling water to non-essential equipment within Unit 3. Fig. 1 (Source: Nuclear Regulatory Commission Plant Information Book) (click to enlarge) Each SW pump is designed to deliver 6,000 gallons of flow. During normal operation, one SW pump can handle the essential loads while two SW pumps are needed for the non-essential loads. Under accident conditions, two SW pumps are needed to cool the essential equipment. The onsite emergency diesel generators can power either of the sets of three pumps, but not both simultaneously. If the set of SW pumps aligned to the essential equipment aren’t getting the job done, workers can open/close valves and electrical breakers to reconfigure the second set of three SW pumps to the essential equipment loops. Because river water can have stuff in it that could clog some of the coolers for essential equipment, each SW pump has a strainer that attempts to remove as much debris as possible from the water. The leak discovered on April 27, 2016, was in the piping between the discharge check valve for SW pump 31 and its strainer. An arrow points to this piping section in Figure 1. The strainers were installed in openings called pits in the thick concrete floor of the intake structure. Water from the leaking pipe flowed into the pit housing the strainer for SW pump 31. The initial leak rate was modest—estimated to be about one-eighth of a gallon per minute. The leak was similar to other pinhole leaks that had occurred in the concrete-lined, carbon steel SW pipes. The owner began daily checks on the leakage and prepared an operability determination. Basically, “operability determinations” are used within the nuclear industry when safety equipment is found to be impaired or degraded. The operability determination for the service water pipe leak concluded that the impairment did not prevent the SW pumps from fulfilling their required safety function. The operability determination relied on a sump pump located at the bottom of the strainer pit transferring the leaking water out of the pit before the water flooded and submerged safety components. The daily checks instituted by the owner included workers recording the leak rate and assessing whether it had significantly increased. But the checks were against the previous day’s leak rate rather than the initial leak rate. By September 18, 2016, the leakage had steadily increased by a factor of 64 to 8 gallons per minute. But the daily incremental increases were small enough that they kept workers from finding the overall increase to be significant. The daily check on October 15, 2016, found the pump room flooded to a depth of several inches. The leak rate was now estimated to be 20 gallons per minute. And the floor drain in the strainer pit was clogged (ironic, huh?) impairing the ability of its sump pump to remove the water. Workers placed temporary sump pumps in the room to remove the flood water and cope with the insignificantly higher leak rate. On October 17, workers installed a clamp on the pipe that reduced the leakage to less than one gallon per minute. The operability determination was revised in response to concerns expressed by the NRC inspectors. The NRC inspectors were not satisfied by the revised operability determination. It continued to rely on the strainer pit sump pump removing the leaking water. But that sump pump was not powered from the emergency diesel generator and thus would not remove water should offsite power become unavailable. Step 5.6.4 of procedure EN-OP-14, “Operability Determination Process,” stated “If the Operability is based on the use or availability of other equipment, it must be verified that the equipment is capable of performing the function utilized in the evaluation.” The operability determination explicitly stated that no compensatory measures or operator manual actions were needed to handle the leak, but the situation clearly required both compensatory measures and operator manual actions. The NRC inspectors found additional deficiencies in the revised operability determination. The NRC inspectors calculated that a 20 gallon per minute leak rate coupled with an unavailable strainer pit sump pump would flood the room to a depth of three feet in three hours. There are no flood alarms in the room and the daily checks might not detect flooding until the level rose to three feet. At that level, water would submerge and potentially disable the vacuum breakers for the SW pumps. Proper vacuum breaker operation could be needed to successfully restart the SW pumps. The NRC inspectors calculated that the 20 gallon per minute leak rate without remediation would flood the room to the level of the control cabinets for the strainers in 10 hours. The submerged control cabinets could disable the strainers, leading to blocked cooling water flow to essential equipment. The NRC inspects calculated that the 20 gallon per minute leak rate without remediation would completely fill the room in about 29 hours, or only slightly longer than the daily check interval. Flooding to depths of 3 feet, 10 feet, and the room’s ceiling affected all six SW pumps. Thus, the flooding represented a common mode threat that could disable the entire service water system. In turn, all safety equipment shown in Figure 2 no longer cooled by the disabled service water system could also be disabled. The NRC estimated that the flooding risk was about 5×10-6 per reactor year, solidly in the Green finding band. Fig. 2 (Source: Nuclear Regulatory Commission Plant Information Book) (click to enlarge) UCS Perspective “Leak before break” is a longstanding nuclear safety philosophy. Books have been written about it (well, at least one report has been written and may even have been read.) The NRC’s approval of a leak before break analysis can allow the owner of an existing nuclear power reactor to remove pipe whip restraints and jet impingement barriers. Such hardware guarded against the sudden rupture of a pipe filled with high pressure fluid from damaging safety equipment in the area. The leak before break analyses can provide the NRC with sufficient confidence that piping degradation will be detected by observed leakage with remedial actions taken before the pipe fails catastrophically. More than a decade ago, the NRC issued a Knowledge Management document on the leak before break philosophy and acceptable methods of analyzing, monitoring, and responding to piping degradation. This incident at Indian Point illustrated an equally longstanding nuclear safety practice of “leak before break.” In this case, the leak was indeed followed by a break. But the break was not the failure of the piping but failure of the owner to comply with federal safety regulations. Pipe breaks are bad. Regulation breaks are bad. Deciding which is worse is like trying to decide which eye one wants to be poked in. None is far better than either. As with the prior Columbia Generating Station case study, this Indian Point case study illustrates the vital role that NRC’s enforcement efforts plays in nuclear safety. Even after NRC inspectors voiced clear concerns about the improperly evaluated service water system pipe leak, Entergy failed to properly evaluate the situation, thus violating federal safety regulations. To be fair to Entergy, the company was probably doing its best, but in recent years, Entergy’s best has been far below nuclear industry average performance levels. The NRC’s ROP is the public’s best protection against hazards caused by aging nuclear power reactors, shrinking maintenance budgets, emerging sabotage threats, and Entergy.Replacing the NRC’s engineering inspections with self-assessments by Entergy would lessen the effectiveness of that protective shield. The NRC must continue to protect the public to the best of its ability. Delegating safety checks to owners like Entergy is inconsistent with that important mission. Support from UCS members make work like this possible. Will you join us? Help UCS advance independent science for a healthy environment and a safer world.