Scenario Earthquakes for Urban Areas Along the Atlantic Seaboard of the United StatesNYCEM
The Sixth Seal: NY City Destroyed
Will the loss be 10 or 100 billion dollars? Will there be 10 or 10,000 fatalities? Will there be 1,000 or 100,000 homeless needing shelter? Can government function, provide assistance, and maintain order?
At this time, no satisfactory answers to these questions are available. A few years ago, rudimentary scenario studies were made for Boston and New York with limited scope and uncertain results. For most eastern cities, including Washington D.C., we know even less about the economic, societal and political impacts from significant earthquakes, whatever their rate of occurrence.
Why do we know so little about such vital public issues? Because the public has been lulled into believing that seriously damaging quakes are so unlikely in the east that in essence we do not need to consider them. We shall examine the validity of this widely held opinion.
Is the public’s earthquake awareness (or lack thereof) controlled by perceived low
Seismicity,
Seismic Hazard, or
Seismic Risk? How do these three seismic features differ from, and relate to each other? In many portions of California, earthquake awareness is refreshed in a major way about once every decade (and in some places even more often) by virtually every person experiencing a damaging event. The occurrence of earthquakes of given magnitudes in time and space, not withstanding their effects, are the manifestations of
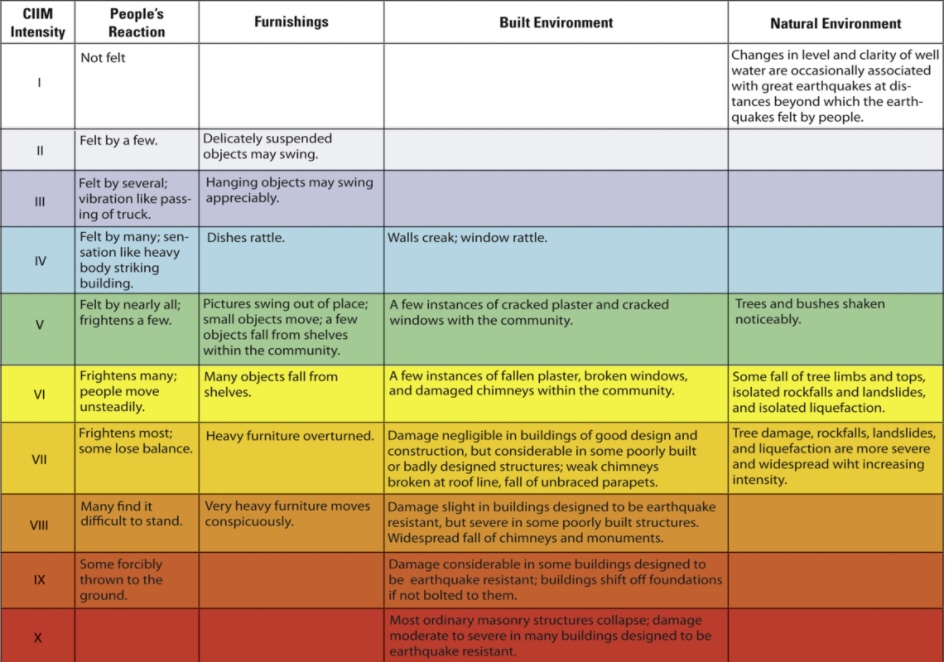
seismicity. Ground shaking, faulting, landslides or soil liquefaction are the manifestations of
seismic hazard. Damage to structures, and loss of life, limb, material assets, business and services are the manifestations of
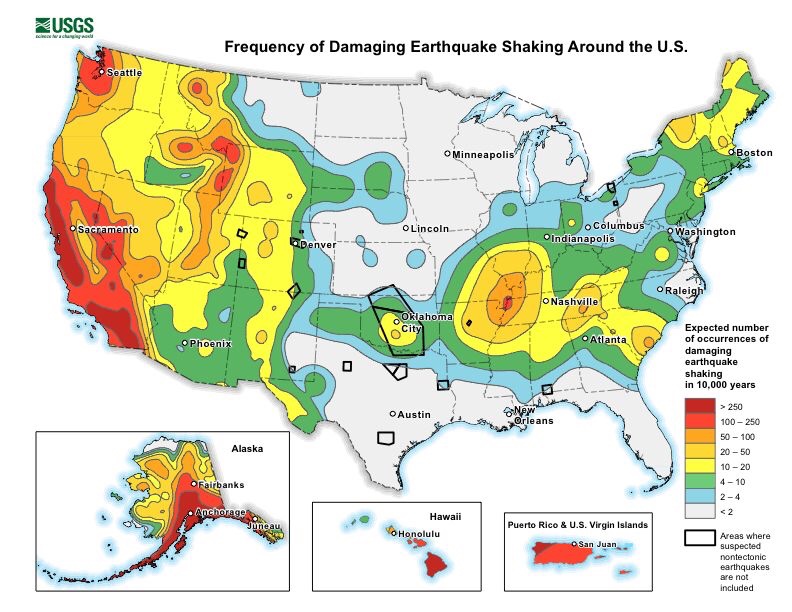
seismic risk. By sheer experience, California’s public understands fairly well these three interconnected manifestations of the earthquake phenomenon. This awareness is reflected in public policy, enforcement of seismic regulations, and preparedness in both the public and private sector. In the eastern U.S., the public and its decision makers generally do not understand them because of inexperience. Judging seismic risk by rates of seismicity alone (which are low in the east but high in the west) has undoubtedly contributed to the public’s tendency to belittle the seismic loss potential for eastern urban regions.
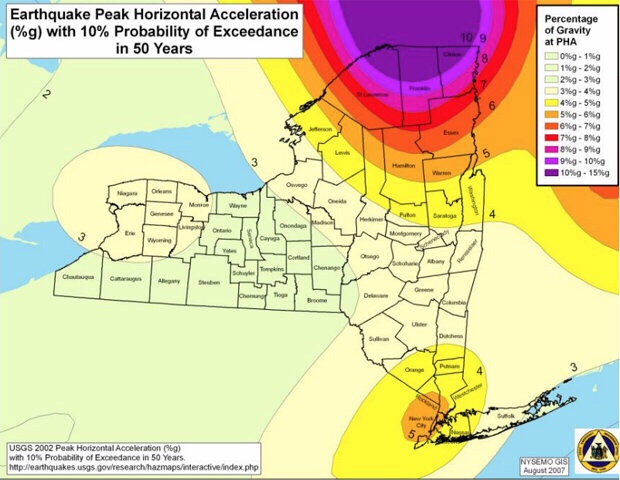
Let us compare two hypothetical locations, one in California and one in New York City. Assume the location in California does experience, on average, one M = 6 every 10 years, compared to New York once every 1,000 years. This implies a ratio of rates of seismicity of 100:1. Does that mean the ratio of expected losses (when annualized per year) is also 100:1? Most likely not. That ratio may be closer to 10:1, which seems to imply that taking our clues from seismicity alone may lead to an underestimation of the potential seismic risks in the east. Why should this be so?
To check the assertion, let us make a back-of-the-envelope estimate. The expected seismic risk for a given area is defined as the area-integrated product of:
seismic hazard (expected shaking level),
assets ($ and people), and the assets’
vulnerabilities (that is, their expected fractional loss given a certain hazard – say, shaking level). Thus, if we have a 100 times lower seismicity rate in New York compared to California, which at any given point from a given quake may yield a 2 times higher shaking level in New York compared to California because ground motions in the east are known to differ from those in the west; and if we have a 2 times higher asset density (a modest assumption for Manhattan!), and a 2 times higher vulnerability (again a modest assumption when considering the large stock of unreinforced masonry buildings and aged infrastructure in New York), then our California/New York ratio for annualized loss potential may be on the order of (100/(2x2x2)):1. That implies about a 12:1 risk ratio between the California and New York location, compared to a 100:1 ratio in seismicity rates.
From this example it appears that
seismic awareness in the east may be more controlled by the rate of seismicity than by the less well understood risk potential. This misunderstanding is one of the reasons why earthquake awareness and preparedness in the densely populated east is so disproportionally low relative to its seismic loss potential. Rare but potentially catastrophic losses in the east compete in attention with more frequent moderate losses in the west. New York City is the paramount example of a low-probability, high-impact seismic risk, the sort of risk that is hard to insure against, or mobilize public action to reduce the risks.
There are basically two ways to respond. One is to do little and wait until one or more disastrous events occur. Then react to these – albeit disastrous – “windows of opportunity.” That is, pay after the unmitigated facts, rather than attempt to control their outcome. This is a high-stakes approach, considering the evolved state of the economy. The other approach is to invest in mitigation ahead of time, and use scientific knowledge and inference, education, technology transfer, and combine it with a mixture of regulatory and/or economic incentives to implement earthquake preparedness. The National Earthquake Hazard Reduction Program (NEHRP) has attempted the latter while much of the public tends to cling to the former of the two options. Realistic and reliable quantitative loss estimation techniques are essential to evaluate the relative merits of the two approaches.
The current efforts in the eastern U.S., including New York City, to start the enforcement of seismic building codes for new constructions are important first steps in the right direction. Similarly, the emerging efforts to include seismic rehabilitation strategies in the generally needed overhaul of the cities’ aged infrastructures such as bridges, water, sewer, power and transportation is commendable and needs to be pursued with diligence and persistence. But at the current pace of new construction replacing older buildings and lifelines, it will take many decades or a century before a major fraction of the stock of built assets will become seismically more resilient than the current inventory is.
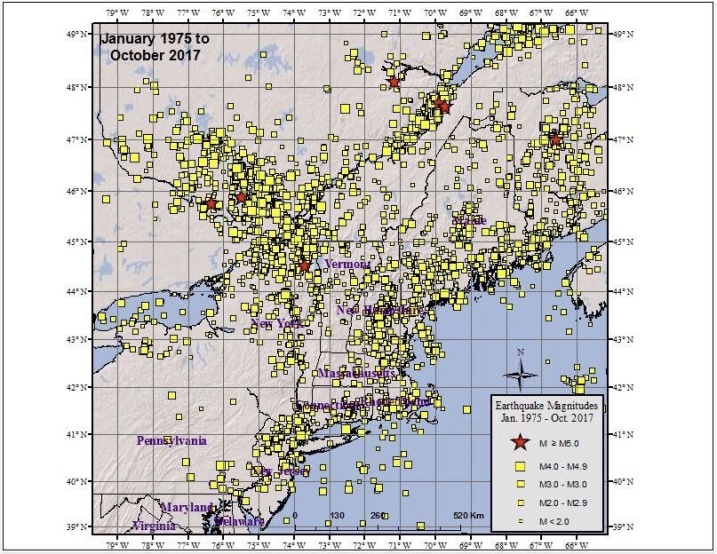
For some time, this leaves society exposed to very high seismic risks. The only consolation is that seismicity on average is low, and, hence with some luck, the earthquakes will not outpace any ongoing efforts to make eastern cities more earthquake resilient gradually. Nevertheless, M = 5 to M = 6 earthquakes at distances of tens of km must be considered a credible risk at almost any time for cities like Boston, New York or Philadelphia. M = 7 events, while possible, are much less likely; and in many respects, even if building codes will have affected the resilience of a future improved building stock, M = 7 events would cause virtually unmanageable situations. Given these bleak prospects,
it will be necessary to focus on crucial elements such as maintaining access to cities by strengthening critical bridges, improving the structural and nonstructural performance of hospitals, and having a nationally supported plan how to assist a devastated region in case of a truly severe earthquake. No realistic and coordinated planning of this sort exists at this time for most eastern cities.The current efforts by the Federal Emergency Management Administration (FEMA) via the National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS) to provide a standard methodology (RMS, 1994) and planning tools for making systematic, computerized loss estimates for annualized probabilistic calculations as well as for individual scenario events, is commendable. But these new tools provide only a shell with little regional data content.
What is needed are the detailed data bases on inventory of buildings and lifelines with their locally specific seismic fragility properties. Similar data are needed for hospitals, shelters, firehouses, police stations and other emergency service providers. Moreover, the soil and rock conditions which control the shaking and soil liquefaction properties for any given event, need to be systematically compiled into Geographical Information System (GIS) data bases so they can be combined with the inventory of built assets for quantitative loss and impact estimates. Even under the best of conceivable funding conditions, it will take years before such data bases can be established so they will be sufficiently reliable and detailed to perform realistic and credible loss scenarios. Without such planning tools, society will remain in the dark as to what it may encounter from a future major eastern earthquake. Given these uncertainties, and despite them, both the public and private sector must develop at least some basic concepts for contingency plans. For instance, the New York City financial service industry, from banks to the stock and bond markets and beyond, ought to consider operational contingency planning, first in terms of strengthening their operational facilities, but also for temporary backup operations until operations in the designated facilities can return to some measure of normalcy. The Federal Reserve in its oversight function for this industry needs to take a hard look at this situation.
A society, whose economy depends increasingly so crucially on rapid exchange of vast quantities of information must become concerned with strengthening its communication facilities together with the facilities into which the information is channeled. In principle, the availability of satellite communication (especially if self-powered) with direct up and down links, provides here an opportunity that is potentially a great advantage over distributed buried networks. Distributed networks for transportation, power, gas, water, sewer and cabled communication will be expensive to harden (or restore after an event).
In all future instances of major capital spending on buildings and urban infrastructures, the incorporation of seismically resilient design principles at all stages of realization will be the most effective way to reduce society’s exposure to high seismic risks. To achieve this,
all levels of government need to utilize legislative and regulatory options; insurance industries need to build economic incentives for seismic safety features into their insurance policy offerings; and the private sector, through trade and professional organizations’ planning efforts, needs to develop a healthy self-protective stand. Also, the insurance industry needs to invest more aggressively into broadly based research activities with the objective to quantify the seismic hazards, the exposed assets and their seismic fragilities much more accurately than currently possible. Only together these combined measures may first help to quantify and then reduce our currently untenably large seismic risk exposures in the virtually unprepared eastern cities. Given the low-probability/high-impact situation in this part of the country, seismic safety planning needs to be woven into both the regular capital spending and daily operational procedures. Without it we must be prepared to see little progress. Unless we succeed to build seismic safety considerations into everyday decision making as a normal procedure of doing business, society will lose the race against the unstoppable forces of nature. While we never can entirely win this race, we can succeed in converting unmitigated catastrophes into manageable disasters, or better, tolerable natural events.