Completed February 5, 2008
(Century 1 Quatrain 27)
The prophecy is more than seeing into the future. For the prophecy sees without the element of time. For the prophecy sees things as they were, as they are, and as they always shall be.



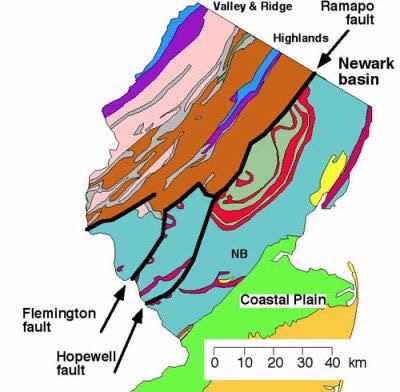
A Look at the Tri-State’s Active Fault Line
Monday, March 14, 2011 
Items lie on the floor of a grocery store after an earthquake on Sunday, August 9, 2020 in North Carolina.
East Coast Quakes: What to Know About the Tremors Below
By Meteorologist Dominic Ramunni Nationwide PUBLISHED 7:13 PM ET Aug. 11, 2020 PUBLISHED 7:13 PM EDT Aug. 11, 2020
People across the Carolinas and Mid-Atlantic were shaken, literally, on a Sunday morning as a magnitude 5.1 earthquake struck in North Carolina on August 9, 2020.
Centered in Sparta, NC, the tremor knocked groceries off shelves and left many wondering just when the next big one could strike.
Fault Lines
Compared to the West Coast, there are far fewer fault lines in the East. This is why earthquakes in the East are relatively uncommon and weaker in magnitude.
That said, earthquakes still occur in the East.
According to Spectrum News Meteorologist Matthew East, “Earthquakes have occurred in every eastern U.S. state, and a majority of states have recorded damaging earthquakes. However, they are pretty rare. For instance, the Sparta earthquake Sunday was the strongest in North Carolina in over 100 years.”
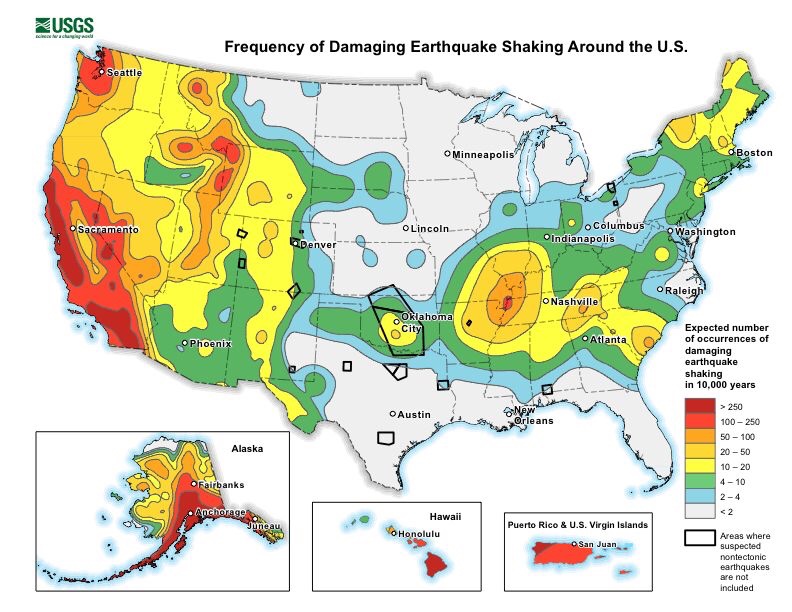
While nowhere near to the extent of the West Coast, damaging earthquakes can and do affect much of the eastern half of the country.
For example, across the Tennesse River Valley lies the New Madrid Fault Line. While much smaller in size than those found farther west, the fault has managed to produce several earthquakes over magnitude 7.0 in the last couple hundred years.
In 1886, an estimated magnitude 7.0 struck Charleston, South Carolina along a previously unknown seismic zone. Nearly the entire town had to be rebuilt.
Vulnerabilities
The eastern half of the U.S. has its own set of vulnerabilities from earthquakes.
Seismic waves actually travel farther in the East as opposed to the West Coast. This is because the rocks that make up the East are tens, if not hundreds, of millions of years older than in the West.
These older rocks have had much more time to bond together with other rocks under the tremendous pressure of Earth’s crust. This allows seismic energy to transfer between rocks more efficiently during an earthquake, causing the shaking to be felt much further.
This is why, during the latest quake in North Carolina, impacts were felt not just across the state, but reports of shaking came as far as Atlanta, Georgia, nearly 300 miles away.

Reports of shaking from different earthquakes of similar magnitude.
Quakes in the East can also be more damaging to infrastructure than in the West. This is generally due to the older buildings found east. Architects in the early-to-mid 1900s simply were not accounting for earthquakes in their designs for cities along the East Coast.
When a magnitude 5.8 earthquake struck Virginia in 2011, not only were numerous historical monuments in Washington, D.C. damaged, shaking was reported up and down the East Coast with tremors even reported in Canada.
Unpredictable
There is no way to accurately predict when or where an earthquake may strike.
Some quakes will have a smaller earthquake precede the primary one. This is called a foreshock.
The problem is though, it’s difficult to say whether the foreshock is in fact a foreshock and not the primary earthquake. Only time will tell the difference.
The United State Geological Survey (USGS) is experimenting with early warning detection systems in the West Coast.
While this system cannot predict earthquakes before they occur, they can provide warning up to tens of seconds in advance that shaking is imminent. This could provide just enough time to find a secure location before the tremors begin.
Much like hurricanes, tornadoes, or snowstorms, earthquakes are a natural occuring phenomenon that we can prepare for.
The USGS provides an abundance of resources on how to best stay safe when the earth starts to quake.


New Evidence Shows Power of East Coast Earthquakes
Virginia Earthquake Triggered Landslides at Great Distances

The Times and Democrat
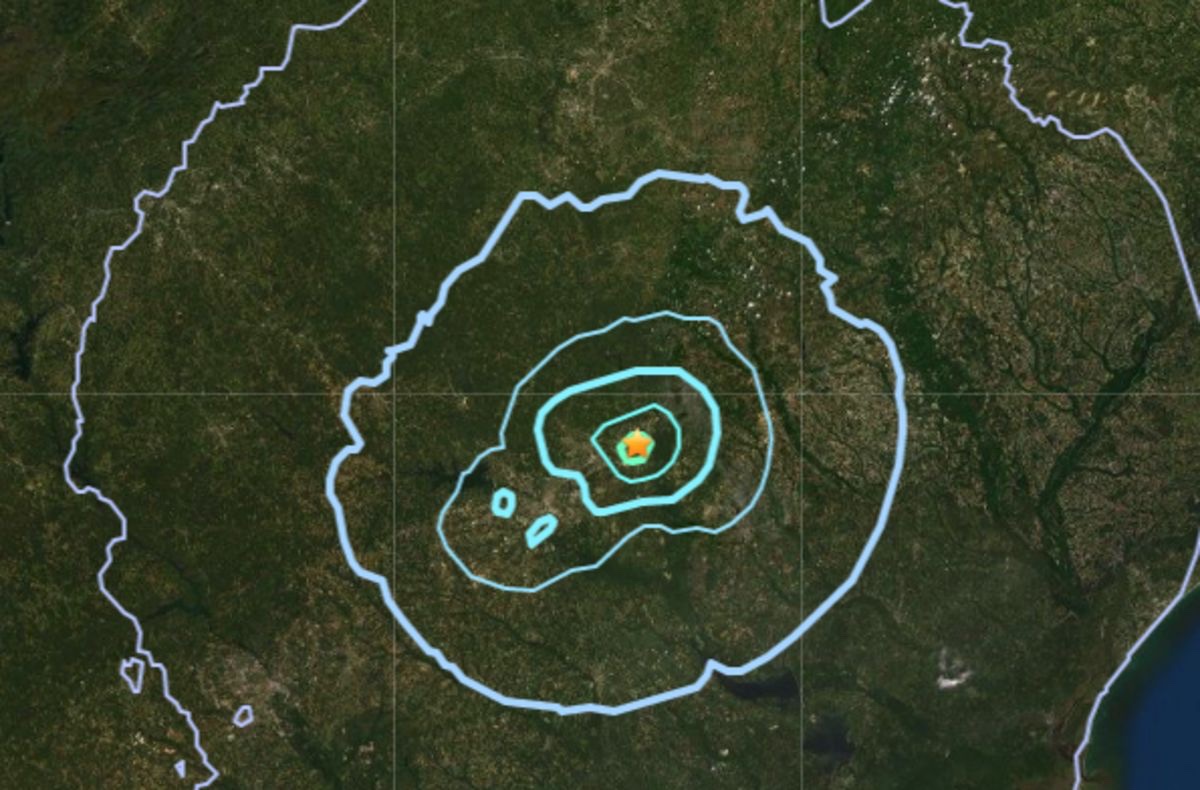
As 2021 ended and 2022 began, a series of minor earthquakes affected South Carolina’s Midlands.
Elgin, a community of fewer than 2,000 residents near the border of Richland and Kershaw counties, has been the epicenter of the seismic activity, starting with a 3.3-magnitude earthquake on Dec. 27. That quake clattered glass windows and doors in their frames, sounding like a heavy piece of construction equipment or concrete truck rumbling down the road.
In January, more earthquakes have been recorded nearby, ranging from 1.5 to a 2.6 in magnitude. No injury or damage was reported.
Now it’s May – and the quakes are back.
In the early hours of May 9, a 3.3 magnitude earthquake shook the ground in Elgin. The earthquake was followed by two back-to-back earthquakes an hour later registering 1.6 and 1.8 magnitudes.
The three quakes pushed South Carolina’s 2022 earthquake tally to 23, with 19 happening within 35 miles of Columbia. Historically, 70% of earthquakes in the state happen along the Coastal Plain, but because the state isn’t considered a hot spot for earthquake activity, the recent midstate quakes are a bit of a mystery.
According to the South Carolina Emergency Management Division, the state typically averages up to 20 quakes each year. Clusters often happen, like six small earthquakes in just more than a week in 2021 near Jenkinsville, about 38 miles west of the most recent group of tremors.
Though quakes are nothing new to South Carolina, many people in the state are not affected. According to emergency management officials, about 70% of South Carolina earthquakes are located in the Middleton Place-Summerville Seismic Zone, about 12.4 miles (20 kilometers) northwest of Charleston.
Every year South Carolina has a week devoted to earthquake preparedness. And there is good reason for awareness.
Aug. 31, 2021, was the 135th anniversary of the largest earthquake to occur in the eastern U.S. In the late evening on that day in 1886, a magnitude 7 earthquake struck near Charleston, causing the loss of more than 100 lives. Many buildings collapsed or were heavily damaged, with economic losses estimated at more than $100 million in today’s dollars.
The quake was felt throughout much of the eastern and central U.S., with people reporting feeling it as far north as New York and as far west as Illinois and Missouri.
In 1999, retired T&D Publisher Dean B. Livingston wrote about what is recorded locally about that “unscheduled” occurrence that had a lot of people singing “Nearer My God To Thee.”
“The area was pounded for a week by quake shocks from four to 12 times a day. The Times and Democrat wrote of the earth’s rumblings: ‘This earthquake frightened many of the inhabitants into deep religious complex, such as was never known before, bringing about a great religious revival in the churches. …’
“One person wrote that ‘many thought the end of the world had come.’ Some terror-stricken citizens in Rowesville ‘ran to and fro exclaiming: ‘The great Judgment Day is at hand. Lord have mercy on me.” A T&D article noted that ‘many people prayed during the past two weeks who never prayed before.’
“A Sawyerdale citizen reported that ‘the flood of accessions to our various churches is almost unparalleled.’
“Residents of the city of Orangeburg were awakened when the first jolt hit. People in brick homes could hear the bricks ‘grinding together as the forces of the shocks increased.’ Many people complained of a nauseous sensation. Chimneys were shaken down, the Baptist church steeple was damaged and for several nights many families slept in the open, under sheds or in small buildings.
“As late as Oct. 14, The T&D reported that ‘shocks have become so common now that people soon throw off the peculiar feeling that they inspire, and go along as if nothing unusual had occurred. There is no telling when they (shocks) will end. …’
“Over in Vance, the quake was described as a ‘sound, a deep, muffled sound … resembling the distant thunder … the earth was one tremendous oscillation. Buildings creaked … poultry squawked, dogs howled, birds chirped; in fact, everything was completely aroused and powerfully demoralized … from 10 to 11 p.m., nine successive shocks were felt.’
“Two Orangeburg men were fishing on the Edisto River when the first big shock hit. They said the first noise sounded like a loud clap of thunder. ‘This was followed by the usual rumbling which was also very loud and deep. The course of the shake was distinctly marked by the falling of the berries and acorns from the trees as it passed.”
While they have no stories comparable to 1886, people of The T&D Region periodically experience tremors. With a large fault in the earth extending from Charleston into the region, when another major quake will come is unpredictable — but practically certain.


East Coast Quakes: What to Know About the Tremors Below
By Meteorologist Dominic Ramunni Nationwide PUBLISHED 7:13 PM ET Aug. 11, 2020 PUBLISHED 7:13 PM EDT Aug. 11, 2020
People across the Carolinas and Mid-Atlantic were shaken, literally, on a Sunday morning as a magnitude 5.1 earthquake struck in North Carolina on August 9, 2020.
Centered in Sparta, NC, the tremor knocked groceries off shelves and left many wondering just when the next big one could strike.

Items lie on the floor of a grocery store after an earthquake on Sunday, August 9, 2020 in North Carolina.
Fault Lines
Compared to the West Coast, there are far fewer fault lines in the East. This is why earthquakes in the East are relatively uncommon and weaker in magnitude.
That said, earthquakes still occur in the East.
According to Spectrum News Meteorologist Matthew East, “Earthquakes have occurred in every eastern U.S. state, and a majority of states have recorded damaging earthquakes. However, they are pretty rare. For instance, the Sparta earthquake Sunday was the strongest in North Carolina in over 100 years.”
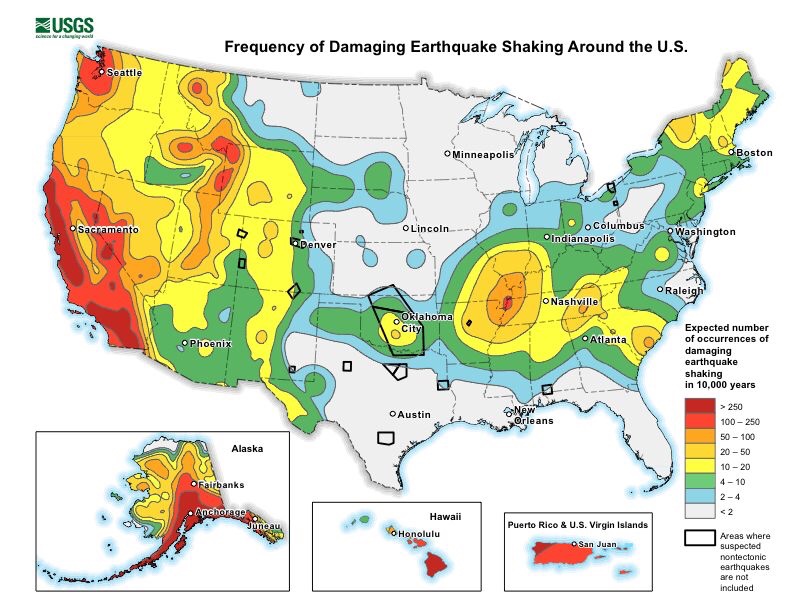
While nowhere near to the extent of the West Coast, damaging earthquakes can and do affect much of the eastern half of the country.
For example, across the Tennesse River Valley lies the New Madrid Fault Line. While much smaller in size than those found farther west, the fault has managed to produce several earthquakes over magnitude 7.0 in the last couple hundred years.
In 1886, an estimated magnitude 7.0 struck Charleston, South Carolina along a previously unknown seismic zone. Nearly the entire town had to be rebuilt.
Vulnerabilities
The eastern half of the U.S. has its own set of vulnerabilities from earthquakes.
Seismic waves actually travel farther in the East as opposed to the West Coast. This is because the rocks that make up the East are tens, if not hundreds, of millions of years older than in the West.
These older rocks have had much more time to bond together with other rocks under the tremendous pressure of Earth’s crust. This allows seismic energy to transfer between rocks more efficiently during an earthquake, causing the shaking to be felt much further.
This is why, during the latest quake in North Carolina, impacts were felt not just across the state, but reports of shaking came as far as Atlanta, Georgia, nearly 300 miles away.
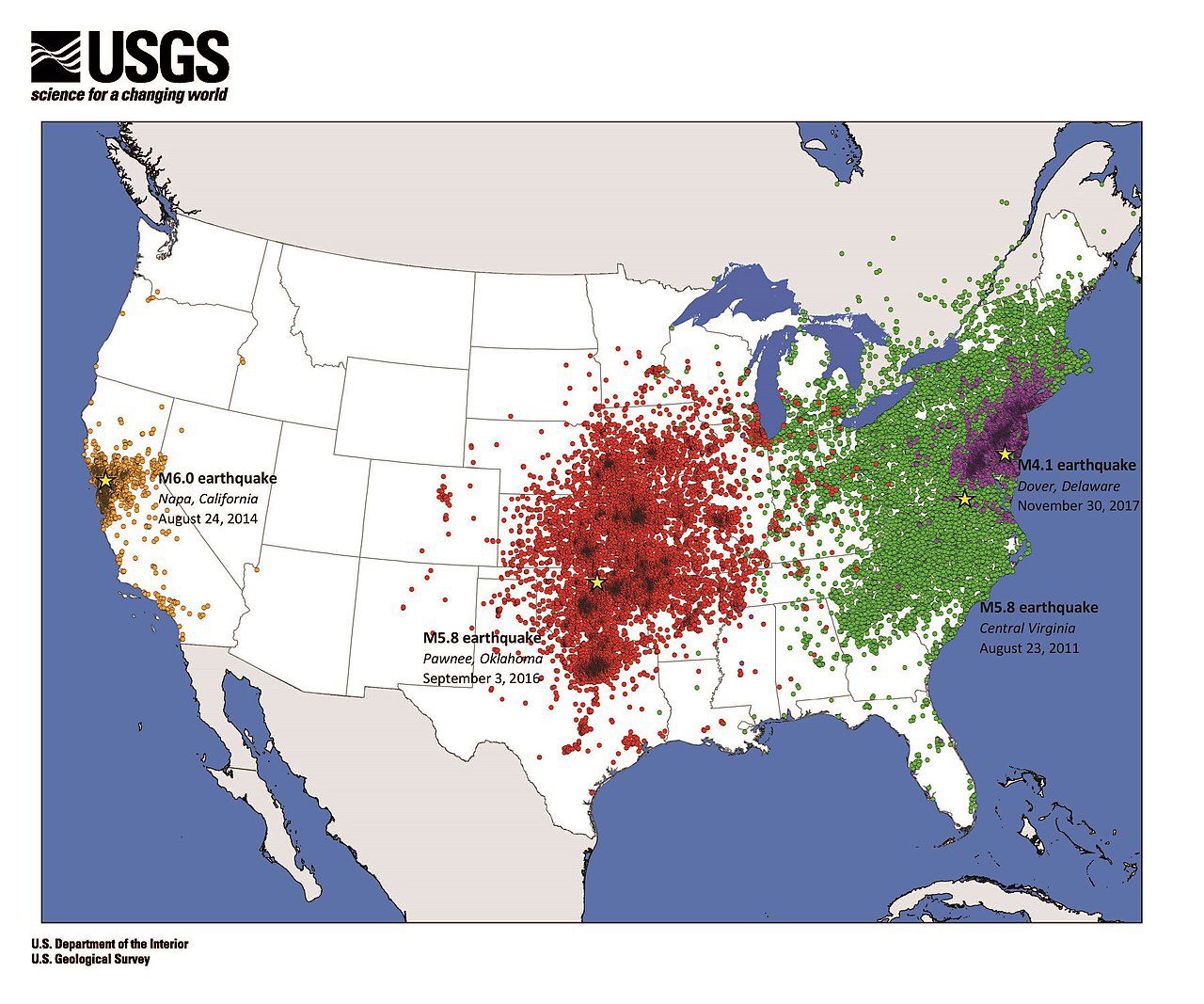
Reports of shaking from different earthquakes of similar magnitude.
Quakes in the East can also be more damaging to infrastructure than in the West. This is generally due to the older buildings found east. Architects in the early-to-mid 1900s simply were not accounting for earthquakes in their designs for cities along the East Coast.
When a magnitude 5.8 earthquake struck Virginia in 2011, not only were numerous historical monuments in Washington, D.C. damaged, shaking was reported up and down the East Coast with tremors even reported in Canada.
Unpredictable
There is no way to accurately predict when or where an earthquake may strike.
Some quakes will have a smaller earthquake precede the primary one. This is called a foreshock.
The problem is though, it’s difficult to say whether the foreshock is in fact a foreshock and not the primary earthquake. Only time will tell the difference.
The United State Geological Survey (USGS) is experimenting with early warning detection systems in the West Coast.
While this system cannot predict earthquakes before they occur, they can provide warning up to tens of seconds in advance that shaking is imminent. This could provide just enough time to find a secure location before the tremors begin.
Much like hurricanes, tornadoes, or snowstorms, earthquakes are a natural occuring phenomenon that we can prepare for.
The USGS provides an abundance of resources on how to best stay safe when the earth starts to quake.